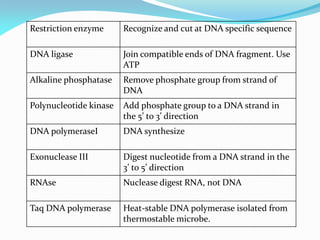
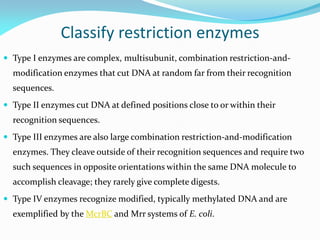
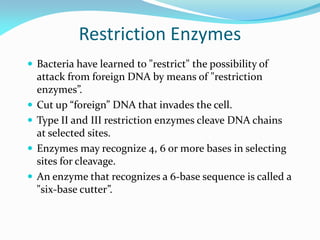
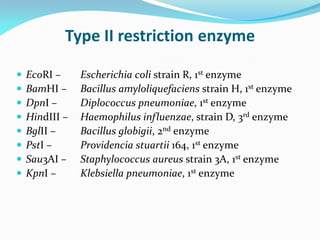
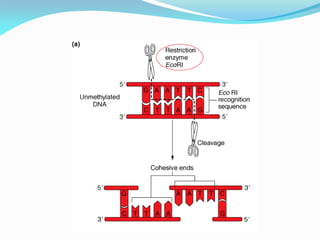
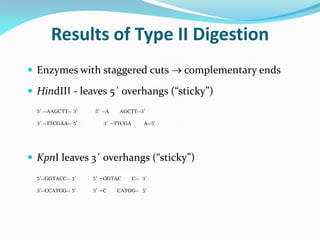
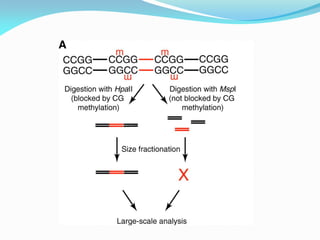
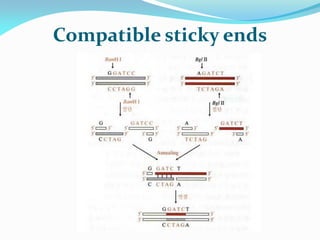
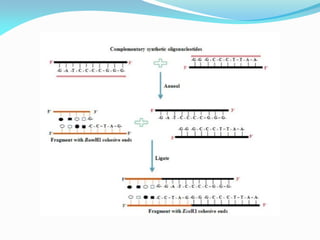
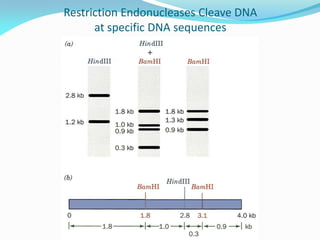
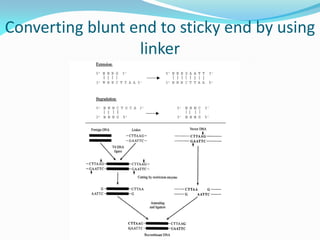
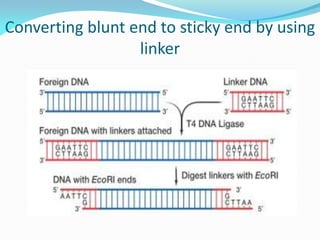
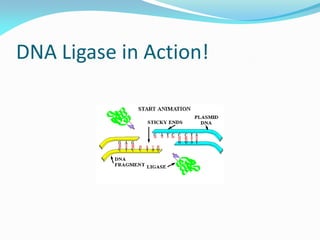
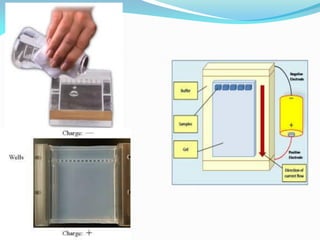
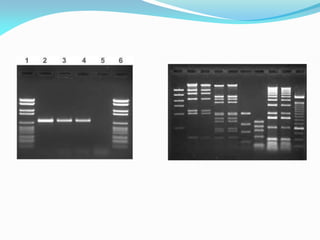
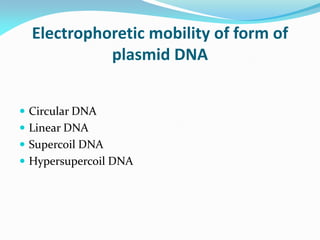
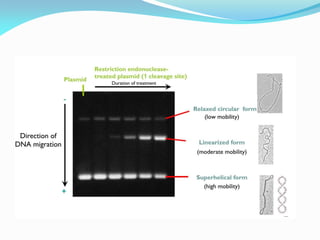
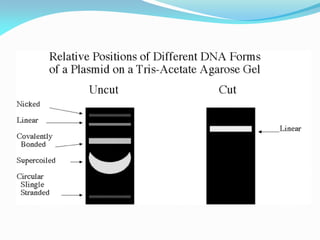
Recombinant DNA technology uses restriction enzymes and DNA ligase to cut and join DNA from different species, generating recombinant molecules that are multiplied in host cells like bacteria. This allows mass production of human proteins like insulin and creation of genetically engineered crops with traits like insect or herbicide resistance. Restriction enzymes recognize short DNA sequences and cut DNA at or near these sites, leaving sticky or blunt ends. DNA can be cut, joined, and modified using various enzymes and techniques to recombine DNA from different sources. Gel electrophoresis is used to separate and analyze DNA fragments by size.