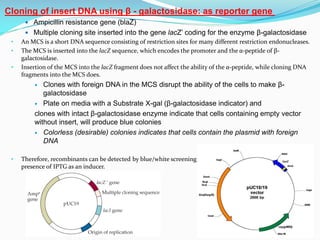
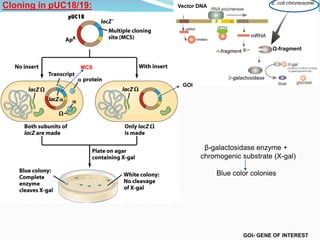
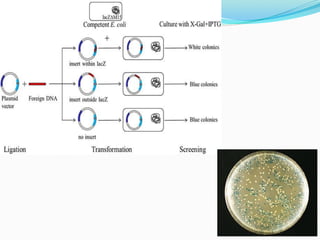
pUC plasmids are small, high copy number cloning vectors developed at the University of California. They contain an ampicillin resistance gene and a multiple cloning site inserted into the lacZ gene. Inserting foreign DNA into the multiple cloning site interrupts the lacZ gene, allowing clones containing inserts to be detected via blue-white screening on media containing X-gal. pUC plasmids are useful cloning vectors due to their high copy number, antibiotic resistance marker, and ability to easily identify recombinant clones.