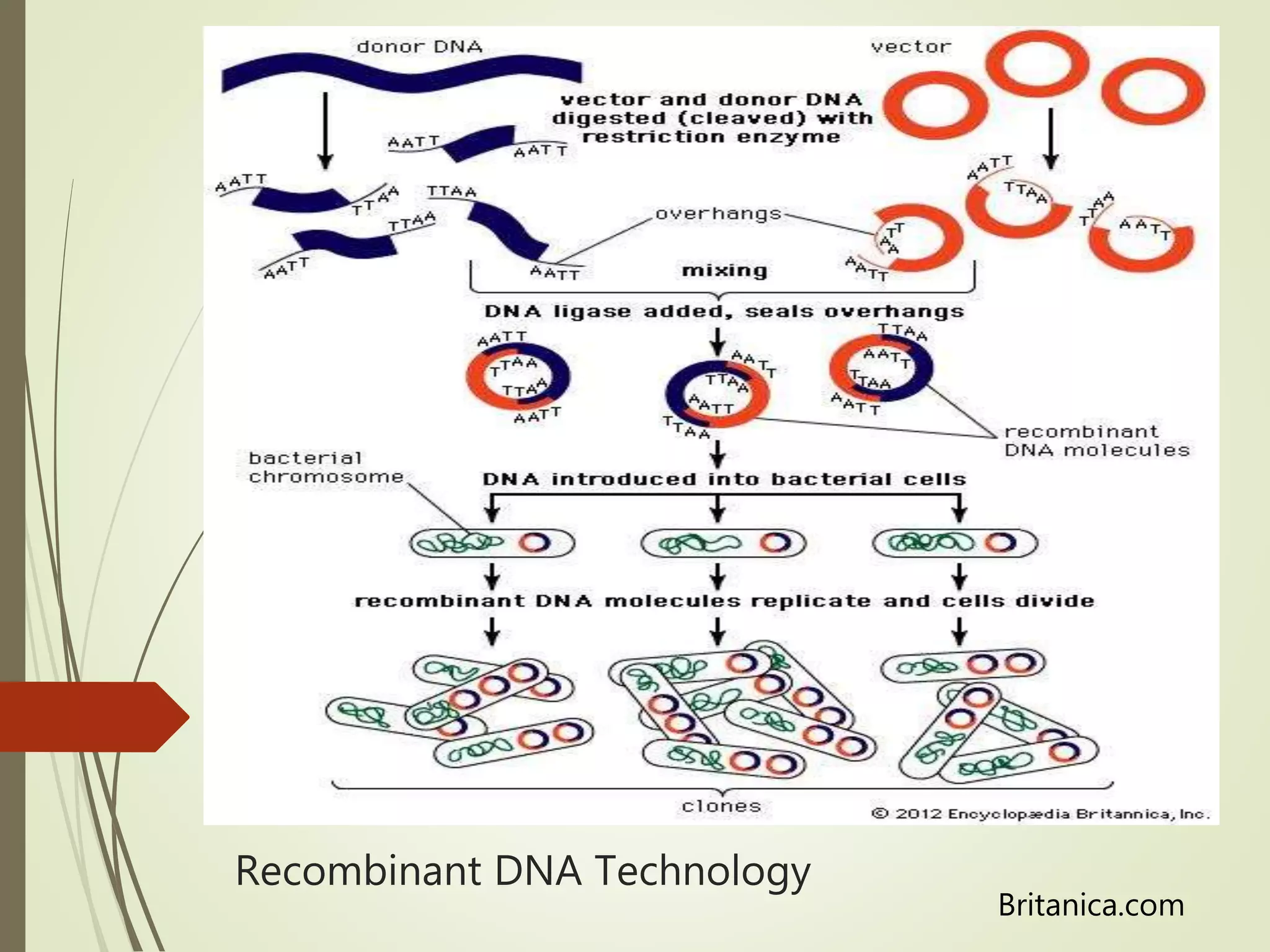
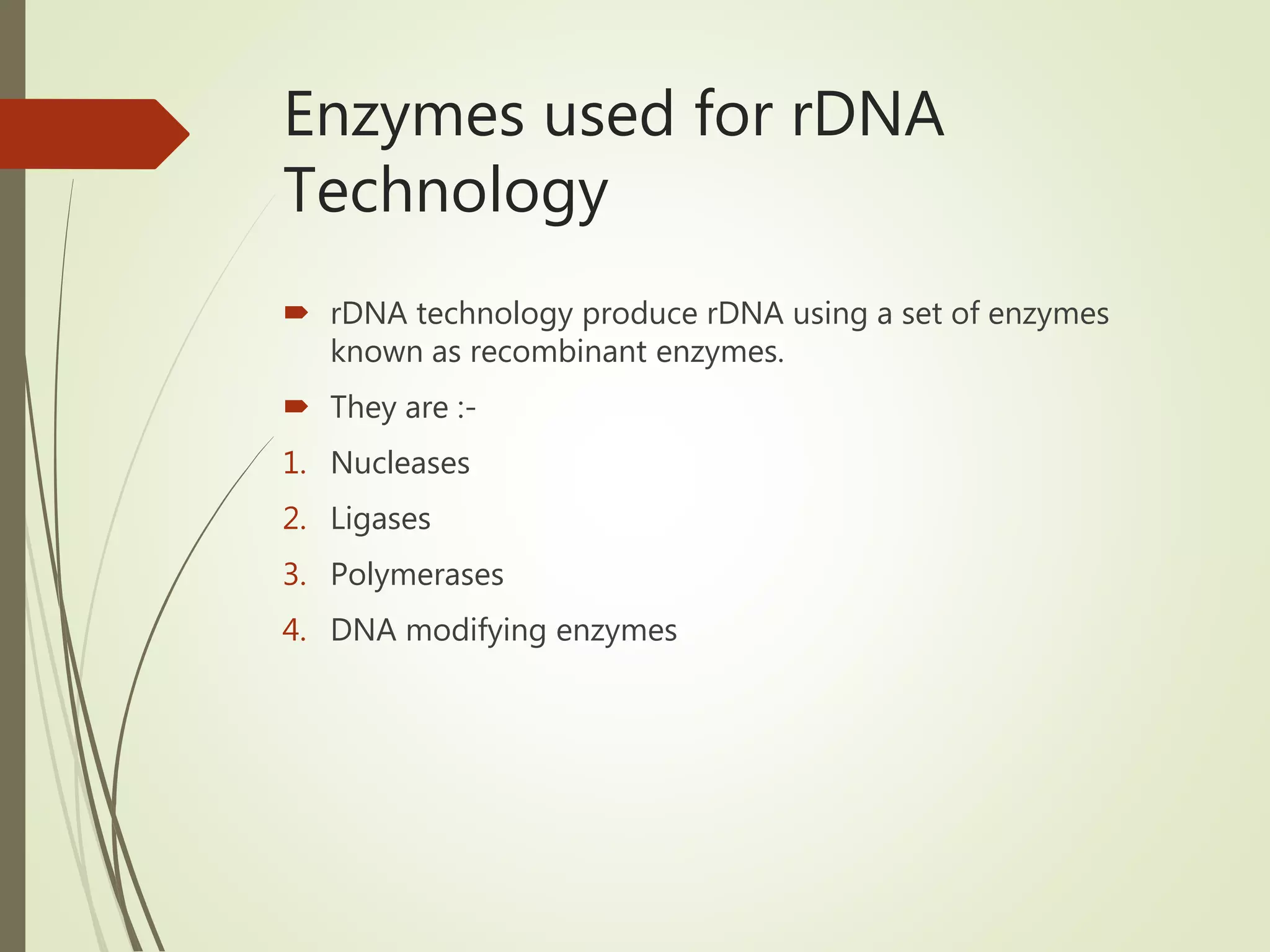
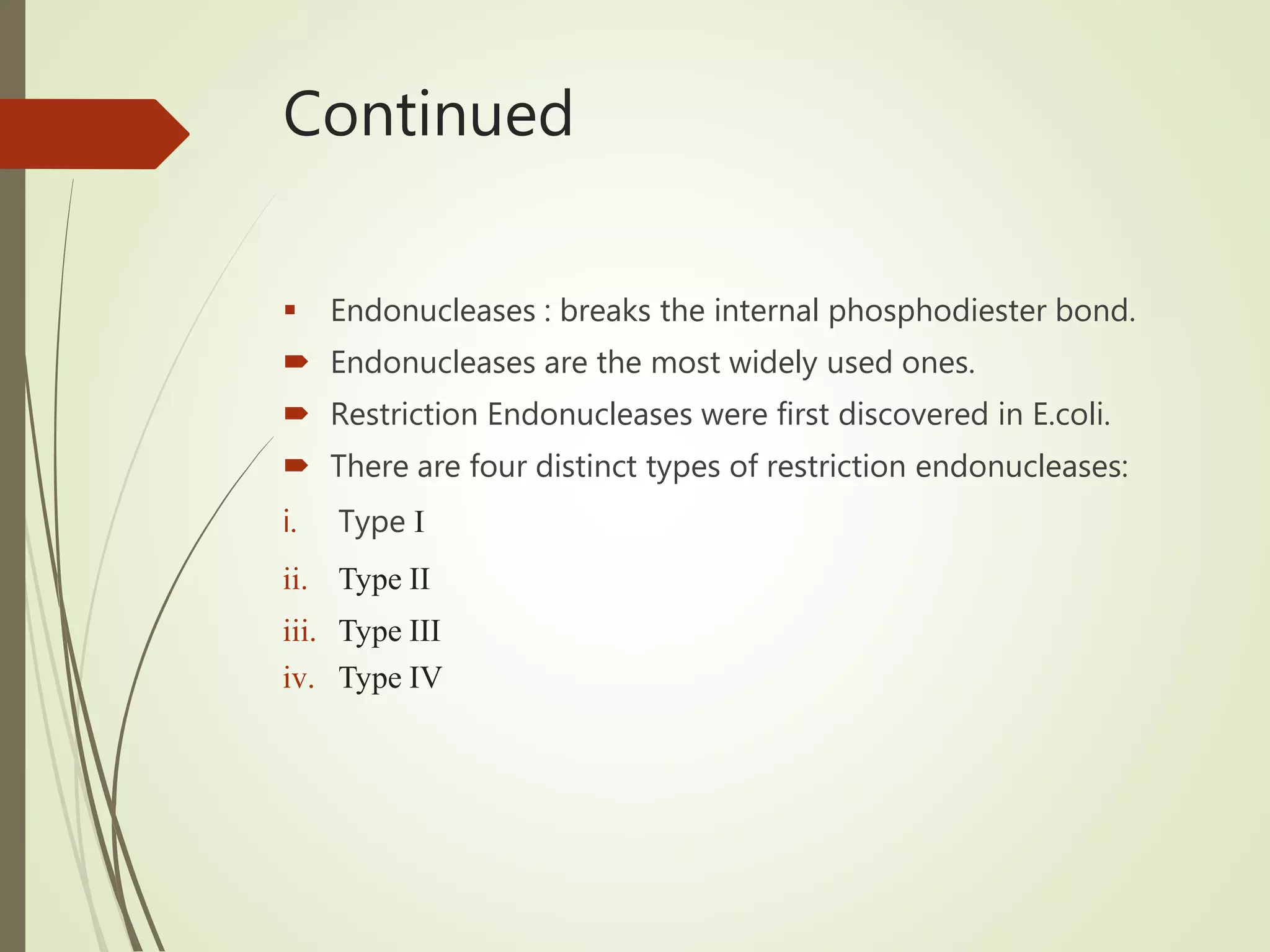
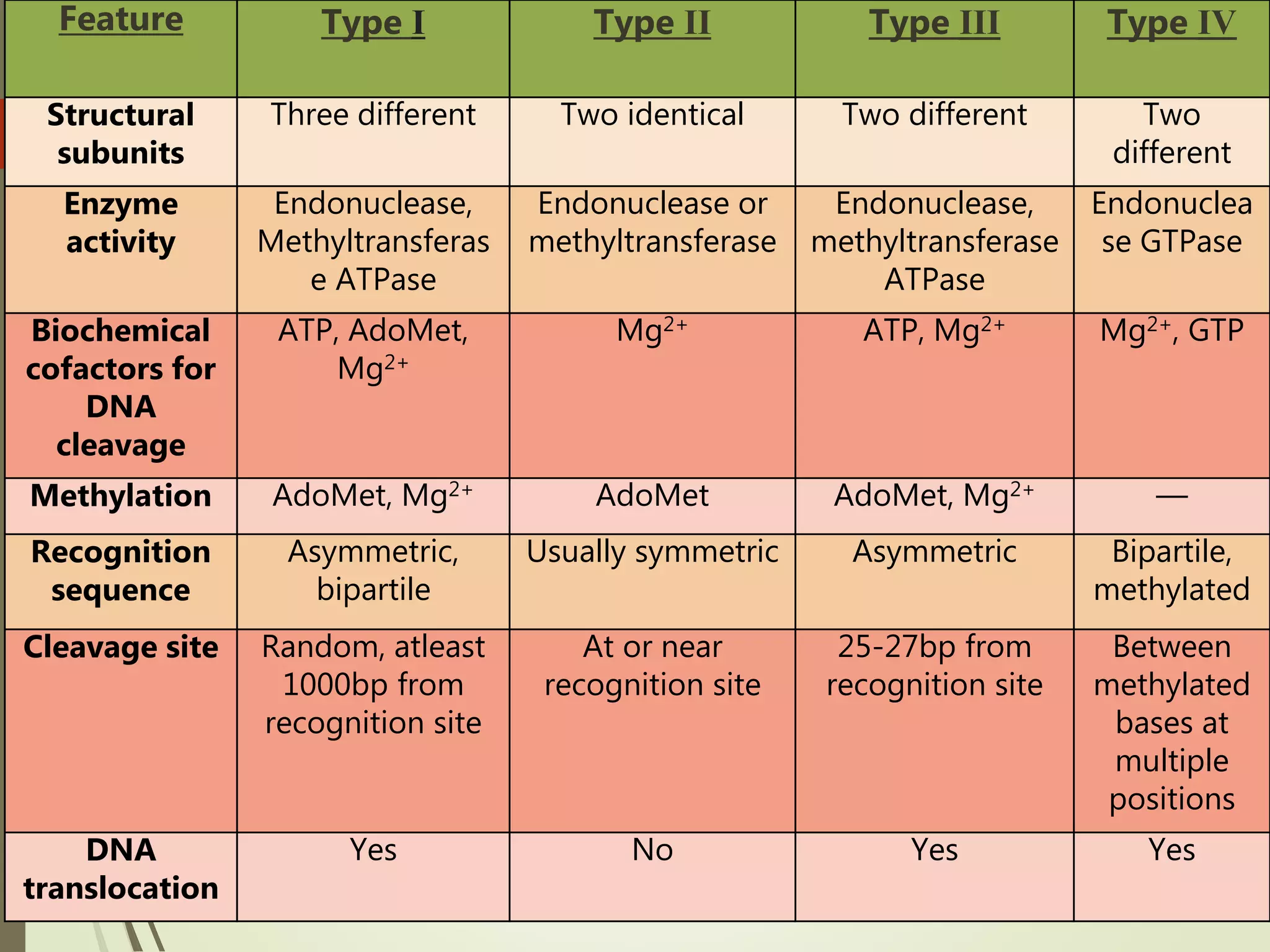
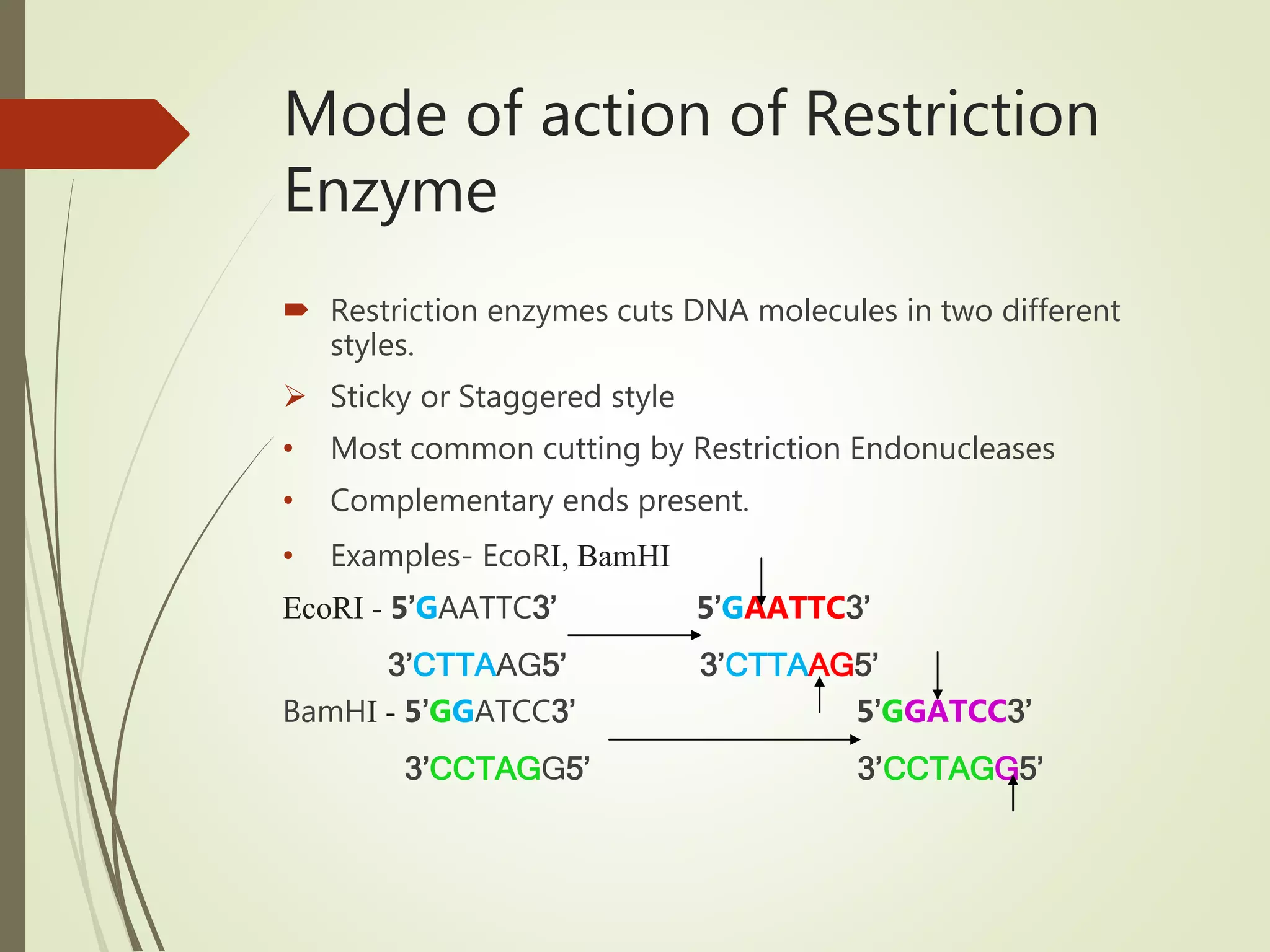
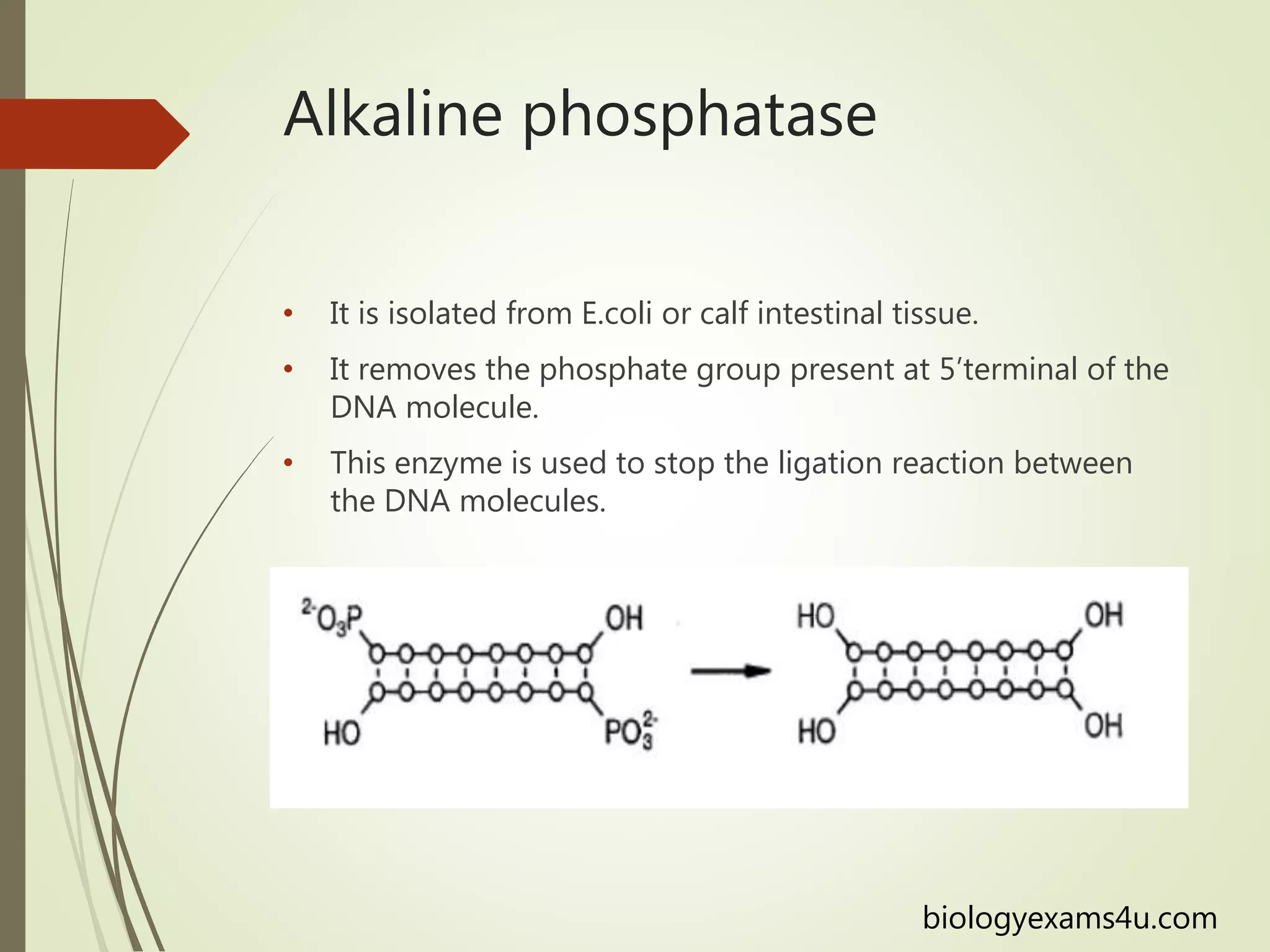
Recombinant DNA technology uses restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, DNA ligase to join DNA fragments, and DNA polymerase to copy DNA. It has many applications including producing vaccines and medicines, DNA fingerprinting, and gene therapy. The basic steps are generating DNA fragments, inserting a fragment into a vector, introducing the vector into host cells, and selecting clones containing the recombinant DNA.