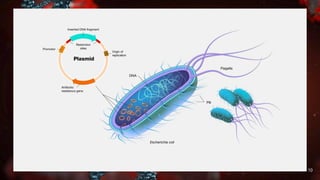
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves manipulating genetic information to enhance desirable traits in organisms, with applications in health, agriculture, and environmental management. This technology has evolved significantly, starting from the discovery of restriction enzymes in the 1960s, and now includes tools like plasmids and cloning techniques. While rDNA offers many benefits, including bioremediation and gene therapy, it also raises biosafety and ethical concerns that necessitate strict regulatory frameworks.