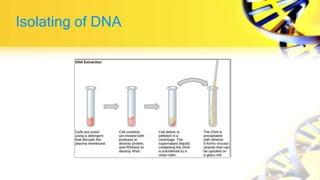
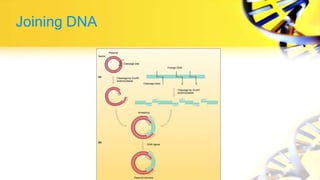
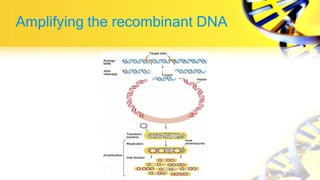
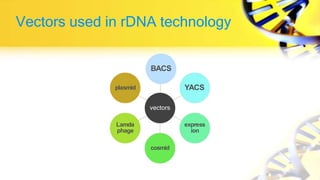
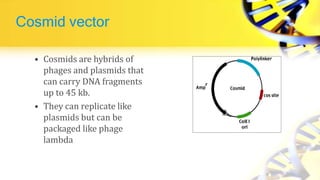
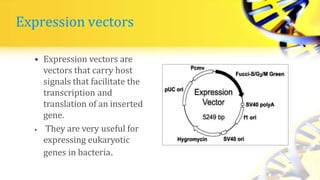
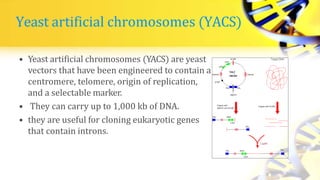
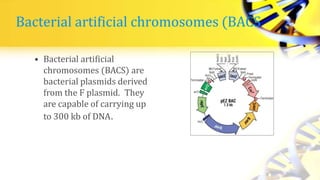
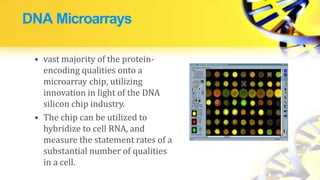
Recombinant DNA technology involves cutting and joining DNA from different sources to produce novel DNA molecules. Some key developments included Watson and Crick discovering the DNA structure in 1953, and Cohen and Boyer producing the first plasmid vector capable of replication in bacteria in 1973. The goals of rDNA technology are to isolate, characterize, alter, and return genes to living cells to understand diseases and improve organisms. Common techniques used include PCR, gel electrophoresis, cloning libraries, and restriction enzyme mapping. Vectors like plasmids, lambda phage, cosmids, and BACs are used to clone and replicate recombinant DNA. Applications include producing medicines like insulin, developing pest-resistant crops, and gene therapy.