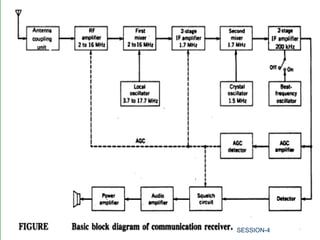
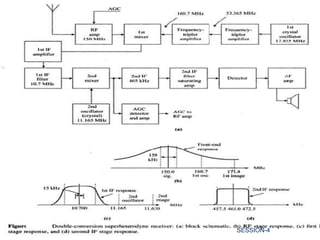
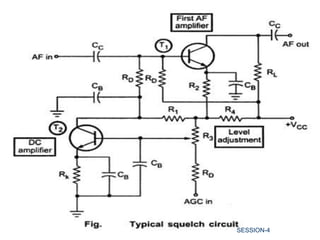
This document discusses various components of communication receivers. It explains that communication receivers are designed for reception of signals used for communication rather than entertainment. It discusses intermediate frequencies used in AM and FM reception and mentions that double conversion receivers provide good image rejection and selectivity for high signal frequencies. It also describes the purpose and operation of a beat frequency oscillator, squelch circuit and automatic gain control in a communication receiver.