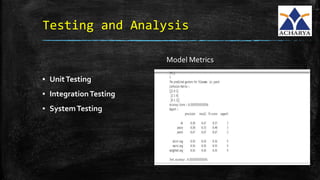
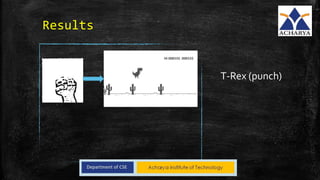
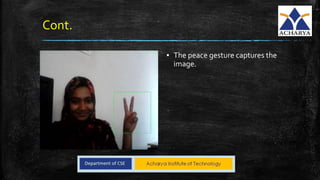
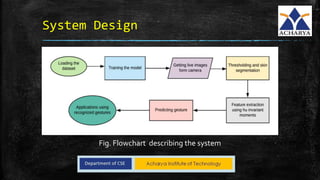
This project developed a gesture recognition application using machine learning algorithms. The application recognizes gestures without color markers by extracting features from images using Hu moments and training a Hidden Markov Model. Common gestures like "ok" and "peace" were mapped to tasks like switching slides. The system was tested and achieved 60% accuracy. Future work could involve adding more gestures and connecting it to other devices.











![Cont.
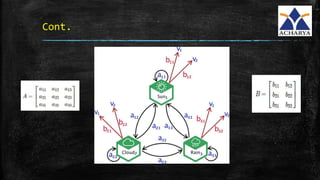
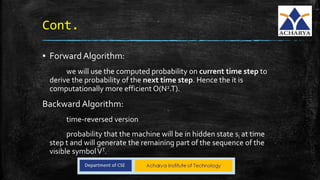
▪ BaumWelch algorithm uses a special case of the Expectation
Maximization(EM) Algorithm.
▪ Steps:
1. Start with initial probability estimates [A,B]. Initially set equal
probabilities or define them randomly.
2. Compute expectation of how often each transition/emission has been
used.We will estimate latent variables [ ξ,γ ] (This is common approach
for EM Algorithm)
3. Re-estimate the probabilities [A,B] based on those estimates (latent
variable).
4. Repeat until convergence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpro-190829162006/85/Hand-Gesture-Recognition-Applications-16-320.jpg)