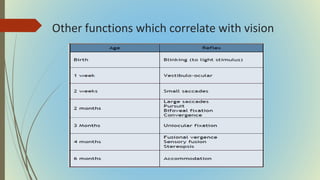
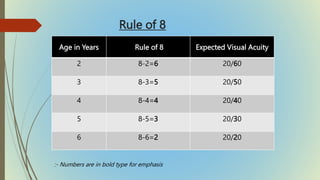
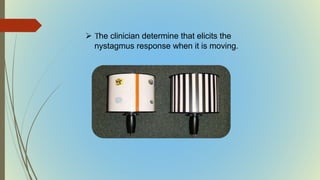
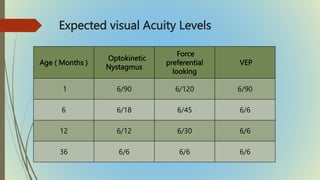
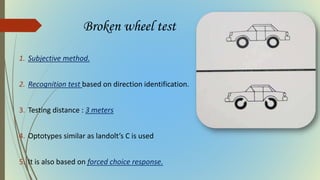
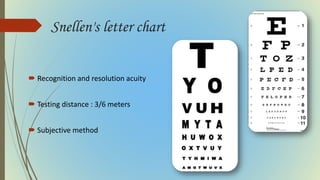
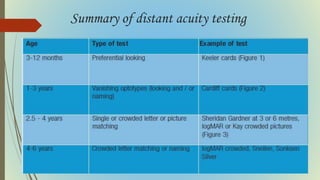
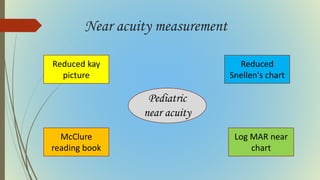
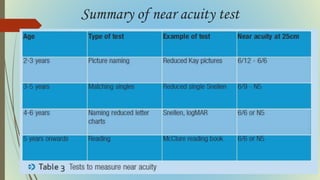
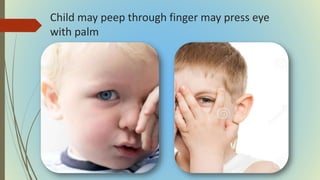
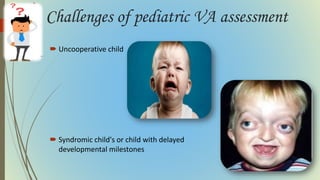
This document provides information on pediatric visual acuity assessment. It discusses various methods used to assess visual acuity in infants, toddlers, preschoolers, and school-aged children. These include optokinetic nystagmus testing, preferential looking tests, Cardiff acuity card testing, visually evoked potentials, and indirect assessment methods. The document outlines the procedures, advantages, and limitations of each method. It also reviews normal visual milestones in infants and children and expected visual acuity levels based on age. Accurate assessment of pediatric visual acuity is important for early detection of eye problems and vision development.