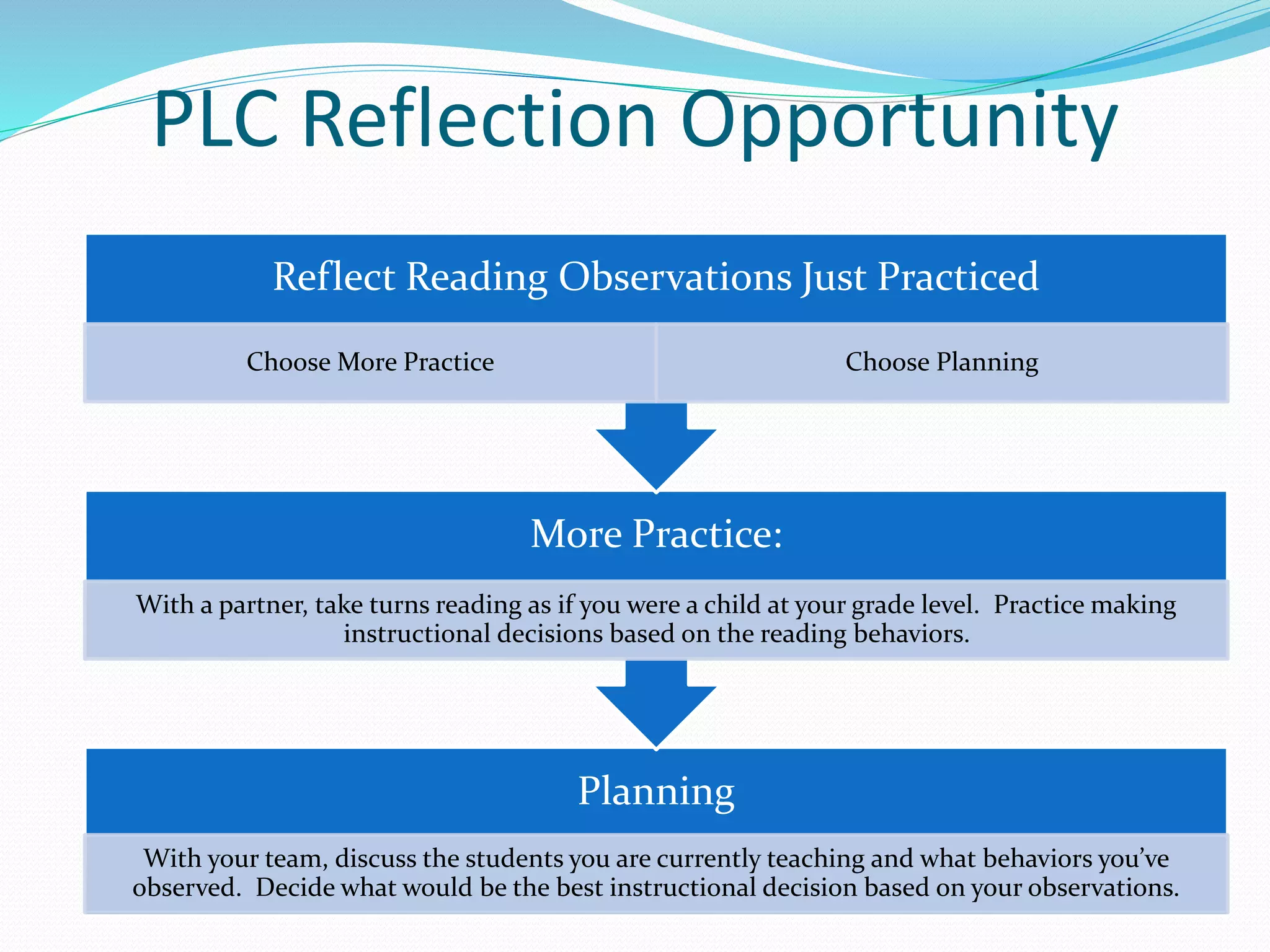
This document provides an agenda and materials for a meeting to discuss implementing a multi-tiered system of reading supports for elementary students. The agenda includes reviewing essential components of elementary reading, using a reading strategies flipbook to observe student reading behaviors and determine their reading stage, and practicing analyzing videos of students reading to determine their stage and plan instruction. Teachers will also have an opportunity for reflection and planning instruction for their own students based on observed reading behaviors.