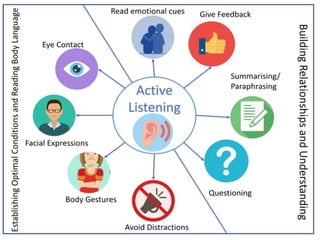
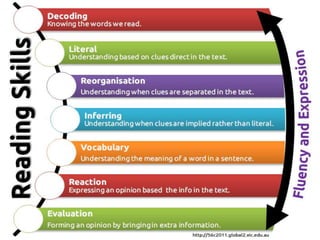
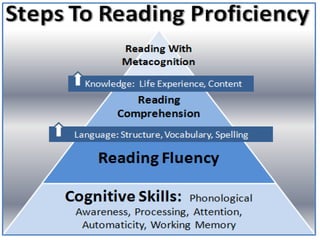
Study skills are important to develop life skills like critical thinking, decision making, and problem solving. Basic skills of communication include listening, reading, writing, and oral presentation. Listening involves receiving and constructing meaning from spoken messages. There are active listening techniques like paying attention and providing feedback. Note taking involves writing down key points from a lecture verbatim, while note making involves understanding and rephrasing the information in your own words. Proper citations and referencing are important to avoid plagiarism when writing essays or research papers.