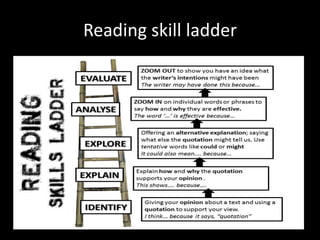
The document provides information on various writing skills and reading comprehension techniques. It discusses the different types of writing such as explorative, descriptive, narrative, persuasive, formal, analytical and chronological writing. It also outlines the key elements of discursive writing such as introduction, background, arguments, counter arguments and conclusion. Additionally, it discusses reading goals, choosing appropriate texts, scanning, skimming and note-taking techniques to improve reading comprehension.