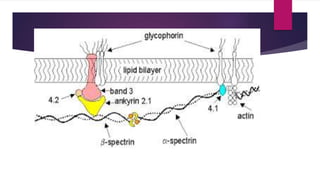
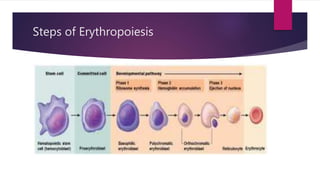
RBCs are biconcave disks that are 62.5% water, 35% hemoglobin, and 2.5% other substances. Their membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer and integral proteins like band-3 and glycophorins. The membrane skeleton, made of spectrin and ankyrin, maintains the biconcave shape and anchors the lipid bilayer. RBCs primarily use glucose through the Embden-Meyerhoff pathway to generate ATP for metabolism. Erythropoiesis occurs in three stages - the mesoblastic, hepatic, and medullary stages - and is regulated by factors like erythropoietin and nutrients.