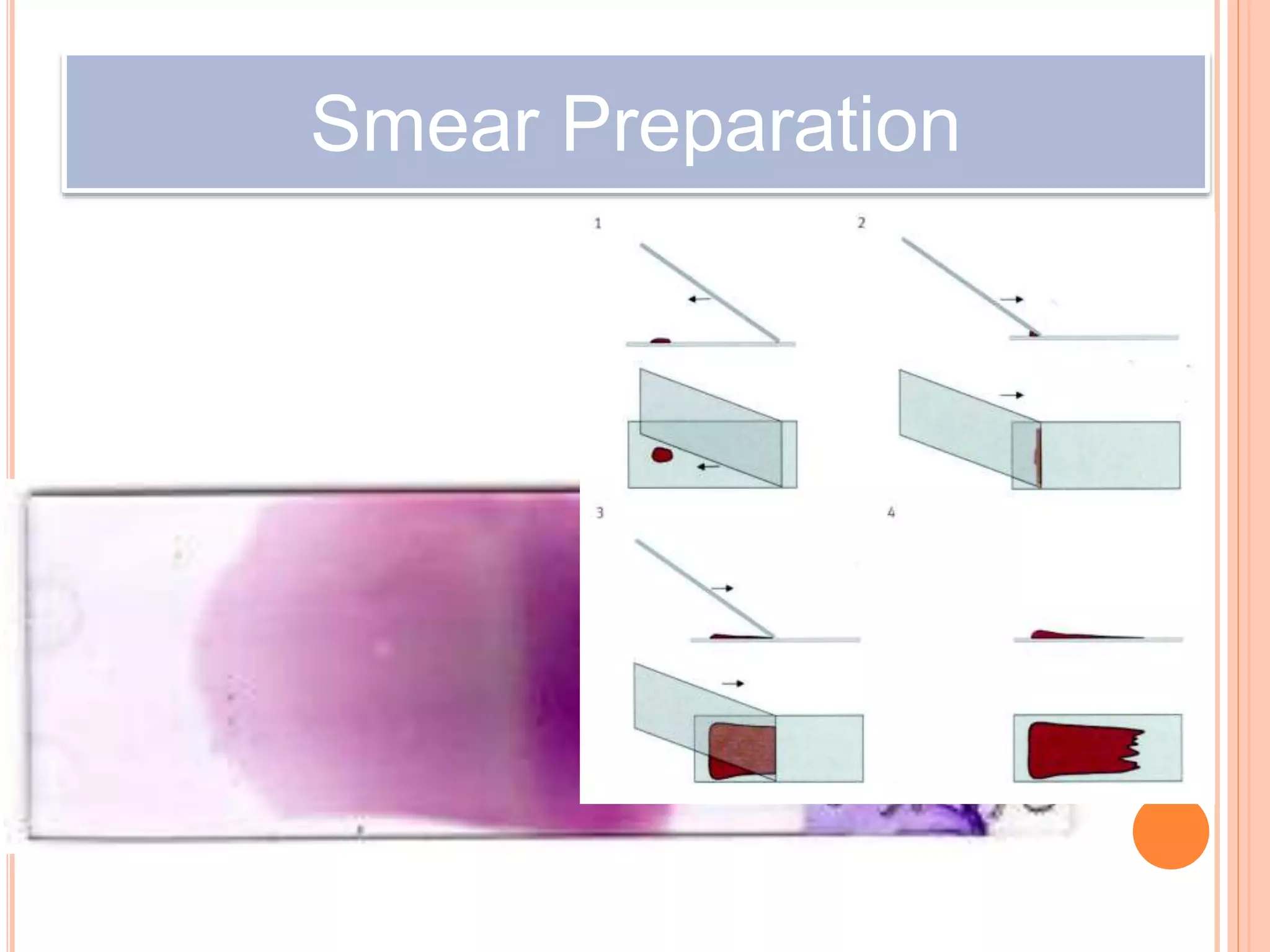
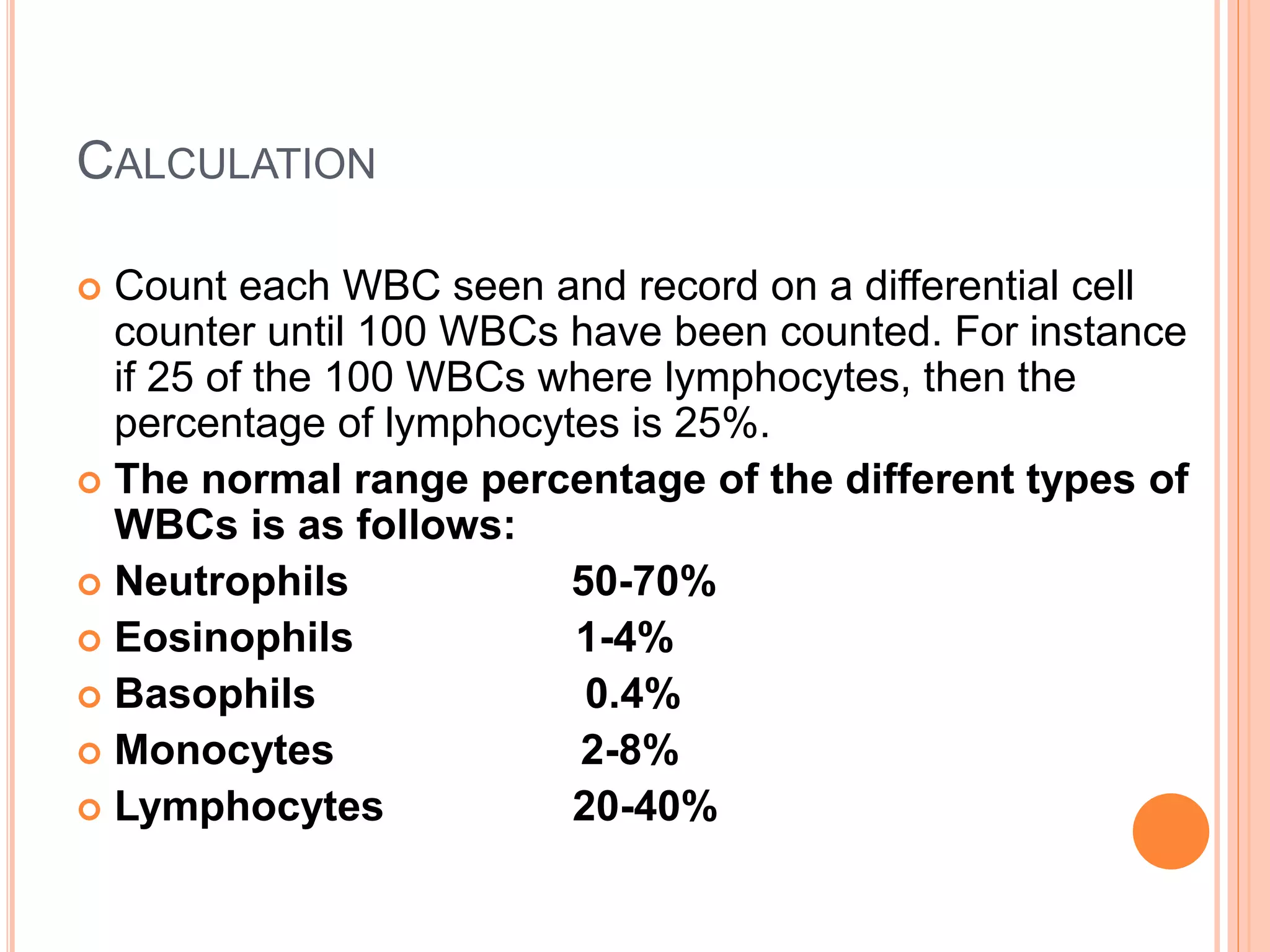
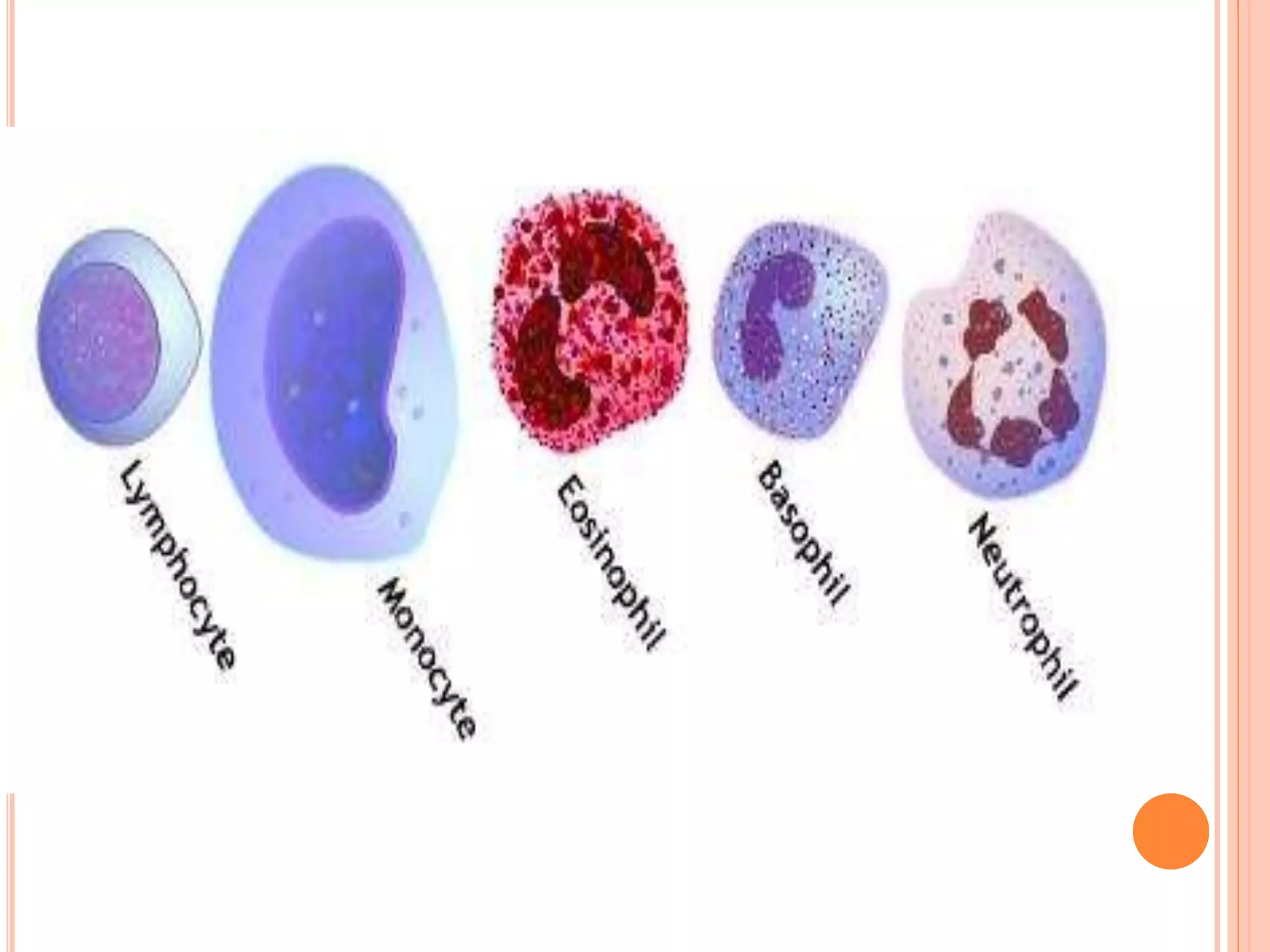
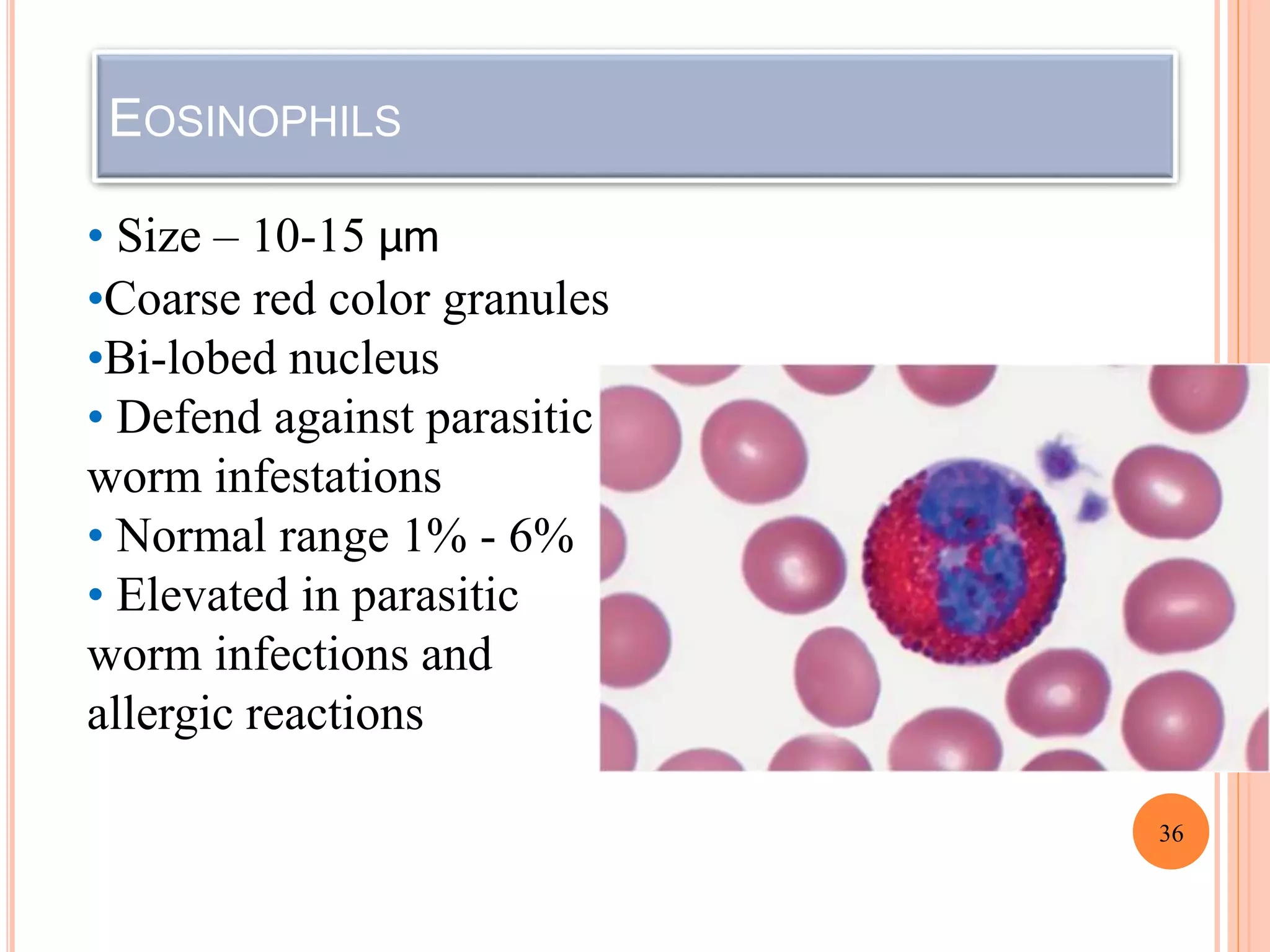
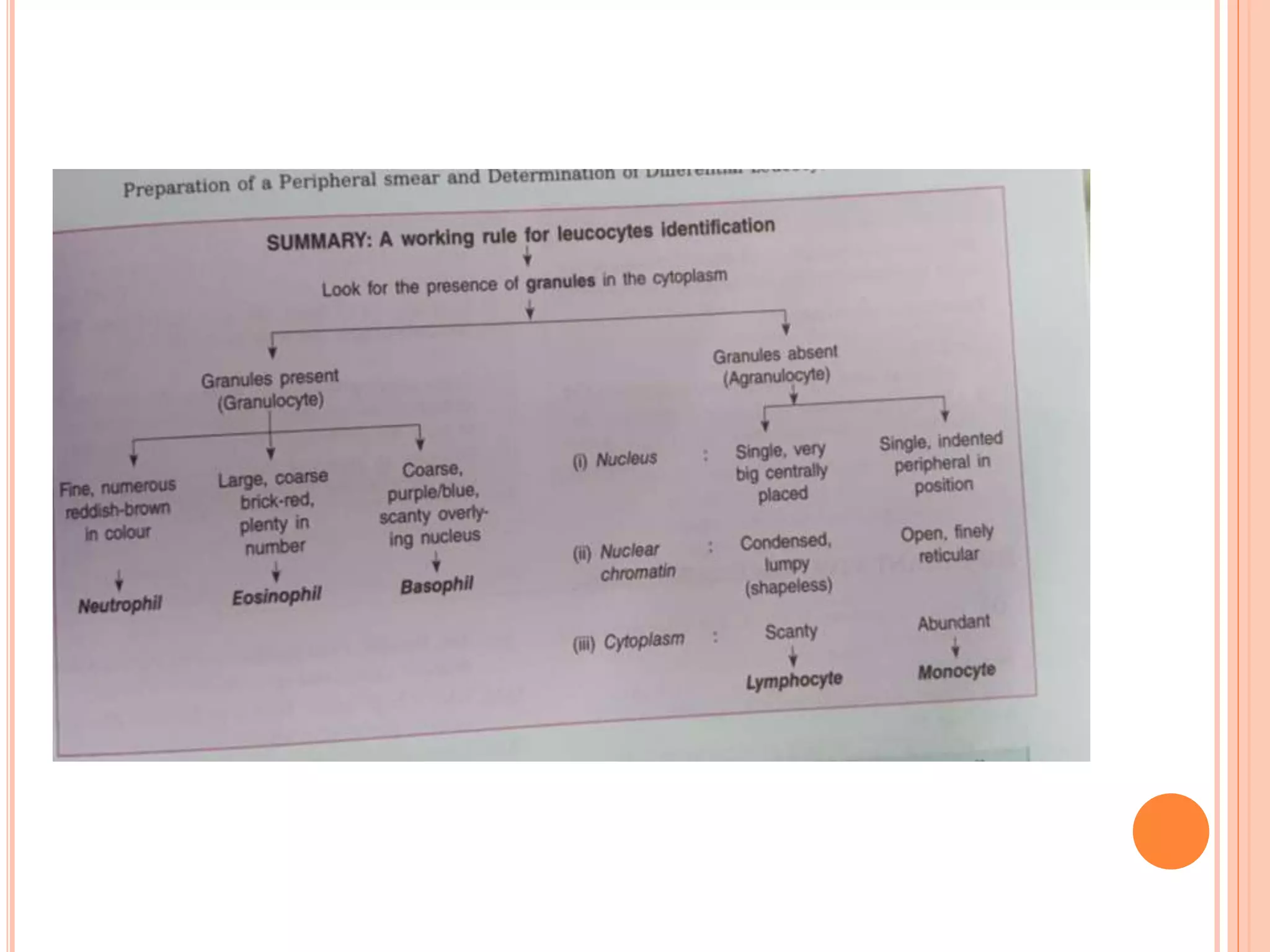
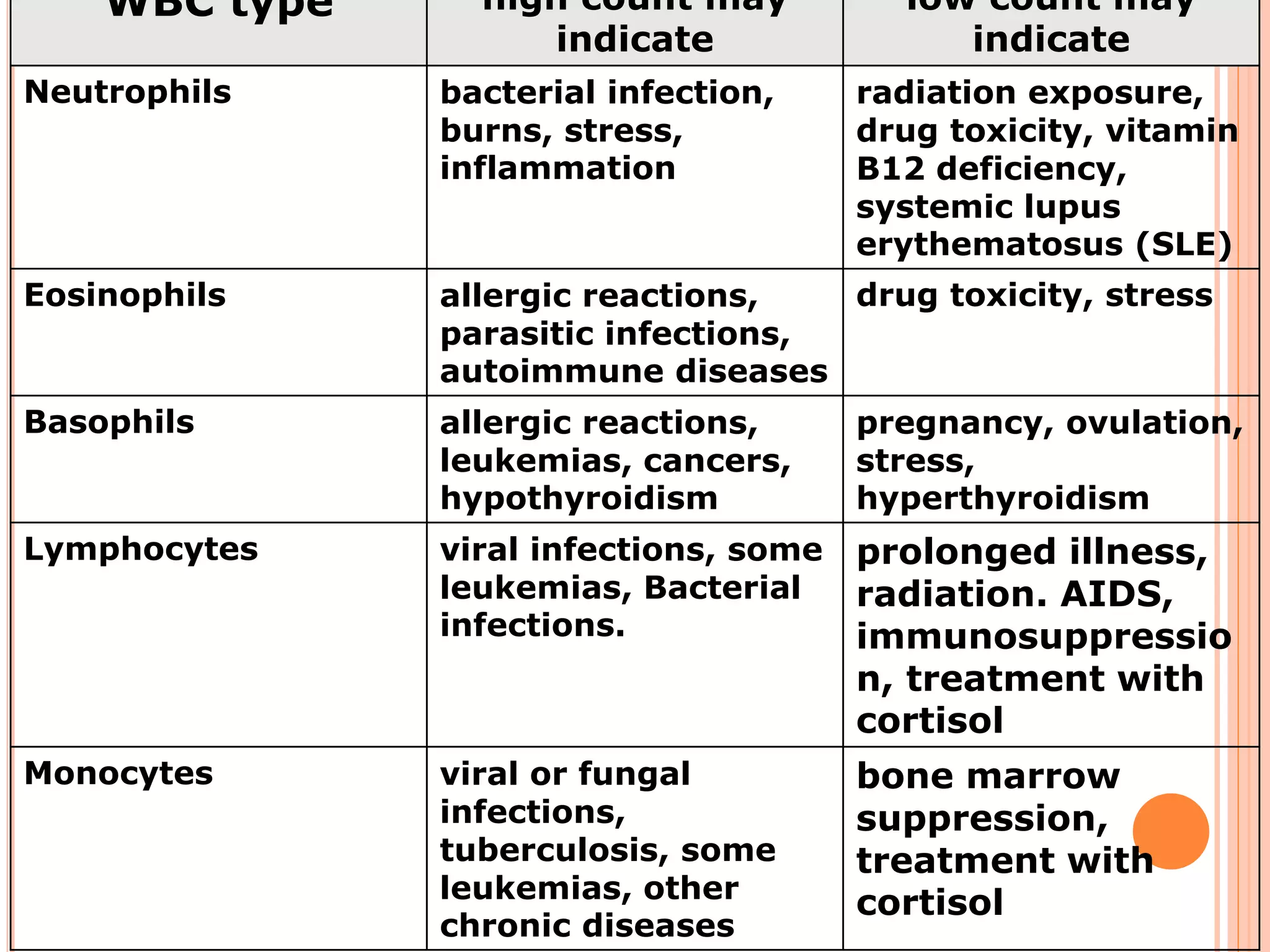
The document describes the process of performing a differential leukocyte count (DLC) from a blood smear. It involves preparing a blood smear, staining it with Leishman's stain, then examining it under a microscope. The key steps are identifying and counting 100 white blood cells to determine the percentage of each type present - neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils. An increased percentage of a particular type can indicate different diseases or infections. The DLC provides information about the immune status and helps diagnose conditions affecting white blood cell levels.