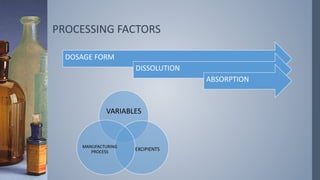
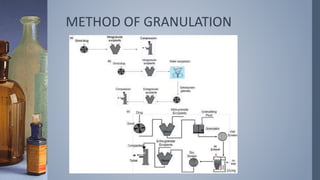
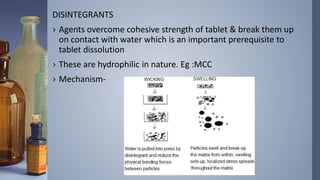
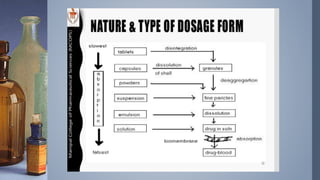
This document discusses factors that influence drug absorption from various pharmaceutical dosage forms. It outlines several formulation variables like excipients, manufacturing processes, dosage form characteristics, and drug properties that can impact the dissolution and absorption of drugs. These variables include excipient type and amount, particle size, polymorphism, compression force, method of granulation, viscosity, and surface area. The document also examines how these factors influence drug absorption from different dosage forms like tablets, capsules, solutions, emulsions, and powders. Understanding these variables is important for developing formulations that effectively deliver drugs to systemic circulation.