Computer based patient record for anaesthesia
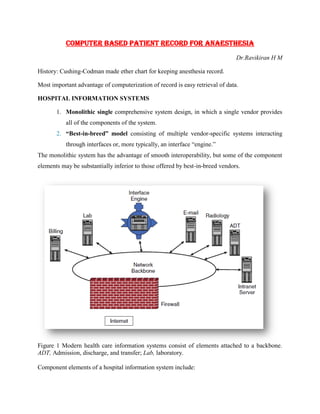
- 1. COMPUTER BASED PATIENT RECORD FOR ANAESTHESIA Dr.Ravikiran H M History: Cushing-Codman made ether chart for keeping anesthesia record. Most important advantage of computerization of record is easy retrieval of data. HOSPITAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS 1. Monolithic single comprehensive system design, in which a single vendor provides all of the components of the system. 2. “Best-in-breed” model consisting of multiple vendor-specific systems interacting through interfaces or, more typically, an interface “engine.” The monolithic system has the advantage of smooth interoperability, but some of the component elements may be substantially inferior to those offered by best-in-breed vendors. Figure 1 Modern health care information systems consist of elements attached to a backbone. ADT, Admission, discharge, and transfer; Lab, laboratory. Component elements of a hospital information system include:
- 2. 1. Administrative 2. Clinical 3. Documentation 4. Billing 5. Business systems ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORD The electronic record has been described variously as a computerized medical record, computerized patient record, electronic medical record, and EHR. Historically, patient records have been controlled or “owned” by hospitals and doctor‟s practices, and their electronic manifestation in the form of the EHR creates a series of issues pertaining to privacy, security, and economic interests of the involved parties. Ideally, the electronic record provides tools for communication among providers. The EHR also should provide immediate access to population-level information for administrative and research applications. Although stand-alone anesthesia information management systems (AIMS) have been in existence for well over a decade, these products have historically functioned in isolation—that is, unintegrated with electronic inpatient or outpatient records. However, with the increased adoption of both inpatient and outpatient EHRs, spurred by federal incentives, desire is growing in the anesthesia community to deploy AIMS that can interface with or be integrated with clinical and billing software (e.g., KLAS report).
- 3. Figure 2 Vendors have developed specialty electronic health records. ED, Emergency department; ICU, intensive care unit. The core functions of EHRs 1. Management of patient health information and data 2. presentation of results acquired from patient testing 3. computerized order entry (CPOE) 4. decision support, whereby automatically generated reminders and prompts are used to guide clinicians and support evidence- based practice 5. communication tools for provider to provider or provider to patient messaging that automatically generate patient support materials such as pamphlets that describe a disease or give discharge directions; 6. integrated administrative processes, including scheduling systems, billing management, and insurancevalidation 7. internal and external reporting requirements are simplified by using the systems built into the EHRs. COMPUTERIZED ORDER ENTRY Prescribing errors are the most common source of adverse drug events, and CPOEs—with or without decision support tools—are widely viewed as being integral to a reduction in errors and improved formulary control.
- 4. Term CPOE is used to refer to computerbased ordering systems designed to automate the ordering process, be it for drugs or for requesting pathologic orradiologic tests. Computerized medication management systems have been designed to cover the entire medication process from prescription to administration, including the following discrete elements: 1. Computerized provider order entry (CPOE) 2. Electronic medication administration record (eMAR) 3. Electronic prescription (ePrescribing) 4. Integrated pharmacy administration systems (which may include pharmacy-based robotic medication dispensing and labeling) 5. Electronic medication reconciliation at each point of patient transition from one environment or provider to another 6. Bar code medication administration matching the right medication to the right patient at the right time Figure 3 Integration of computerized order entry (CPOE) into the workflow of an organization.
- 5. Figure 4 Various benefits of a computerized order entry (CPOE). DATA REGISTRIES Electronic records, order entry systems, and automated device interfaces are several mechanisms by which the data associated with anesthesia care can be captured and subsequently used to populate data repositories. These data may then be stored in a local, vendor-specific data store (i.e., in an AIMS-specific database), ported to a hospital or system data “store” and integrated with other data sources, or extracted to a multiinstitutional registry such as the Multicenter Perioperative Outcomes Group (MPOG)* hosted at the University of Michigan. MPOG is an academic consortium “aggregating large volumes of observational inpatient electronic health record data, patient reported outcomes and long term administrative outcomes.” Data repositories may be used to analyze and track individual patients, groups of patients, or pathologic conditions. Much as the availability of large, comprehensive data sets has transformed other industries by enabling, for example, sophisticated pattern recognition algorithms that can detect fraud, analyzing purchasing patterns, or projecting election outcomes, perioperative data registries have been used to evaluate perioperative practices.
- 6. The Anesthesia Quality Institute created a nationwide system to collect data about adverse events relating to anesthesia, pain management, and perioperative care in 2011. The system is called the Anesthesia Incident Reporting System (AIRS) and represents a data registry designed to collect information about anaphylactic reactions, device malfunctions, medication side effects, unusual vascular or neurologic injuries, and complications relating to the use of EHRs in anesthesia settings. Data are submitted anonymously or confidentially over a secure, encrypted Internet link and used for educational purposes or for monitoring emerging trends in anesthesia patient safety relating to new medications and techniques, data records, or patient risk factors. DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Decision support tools integrated into the EHR and CPOE can provide immediate access to current medical knowledge, institutional best practices, billing compliance information, and administrative functions and can facilitate cost control. Although a wide range of architectures are used, DSSs fall somewhere on the spectrum between expert systems, in which rules developed by domain experts are used to drive decision support, and autonomous systems that have the ability to “learn” and make observations about large data sets. An example of the latter might be a system that automatically culls through a physician‟s orders to develop a profile of prescribing patterns. A DSS can “act” in one of three ways. 1. It may be a passive system that responds with information when asked. 2. Alternatively, it may be semiactive and provide alerts or alarms only when certain conditions are met. 3. Finally, a system may be active and autonomous and generate an order set or manage a medical process automatically, such as automated weaning of mechanical ventilation according to built-in rules.
- 7. Figure 5 Various barriers to adoption of electronic health records. REFERENCE: Miller’s anesthesia-8th edition Medical records Pertains to documents containing a chronological written account of the patient‟s medical history and complaints, physical findings, results of diagnostic tests, medications, therapeutic procedures and day-wise progress notes recorded by a medical practitioner. It is a part of medical training and one must make a habit of keeping records, not only in the interest of medical science, but also for his own safety and interest. It serves as a documentary evidence of the patient‟s illness, treatment and response to the treatment. This record may be used as evidence in malpractice suits, claims of the insurances and compensations in personal injury suits. The dictum is that „If it is not in the record—it did not occur’.
- 8. Records are the property of the hospital and the personal data contained in the medical record is considered confidential information and the property of the patient. Original hospital record of the medico-legal case (MLC) including X-ray/CT/MRI films should not be handed over to the police. However, if the investigating officer requests, a photocopy of the record (bed-head-ticket) may be supplied and a receipt of the same must be obtained. „„ Medico-legal report (MLR) and postmortem report (PMR) belongs to the requestor, i.e. the police and the same is held by the doctor in fiduciary relationship. If affected party is asking for a record, then attested photocopy of the MLR can be handed over to the patient or his/her relative and after the requisite fee has been paid by applicant. Request for supply of copy of MLR or PMR under the RTI Act are not maintainable under Section 8(1) (e) & Section 8(1) (h). It should not be issued to third parties (including the accused) by the hospital authorities. Safe custody of the patient‟s confidential records, whether kept in conventional manner or in a computer, is the responsibility of the doctor. Patient‟s record cannot be used in clinics or conferences without the patient‟s consent. Hospitals have the right to use the records without consent for evaluating the quality of care and statistical purposes. X-ray films are the property of the hospital/doctor as part of the record, the patient is entitled for the skill and treatment, but copies of records and X-ray films may be given. Under the Directorate General of Health Services guidelines published in „Hospital Manual‟, the responsibility of hospital to keep medical records is upto 5 years for outpatient department, and for inpatient medical records (including case sheets of medico-legal cases) it is upto 10 years.
