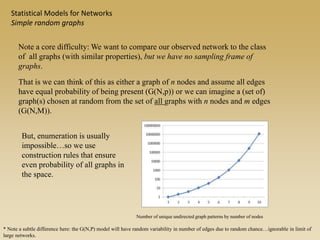
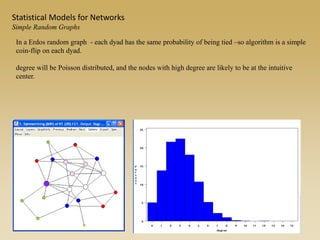
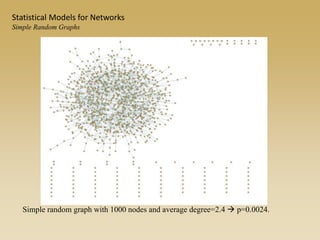
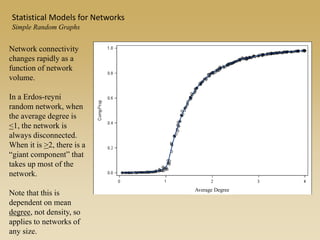
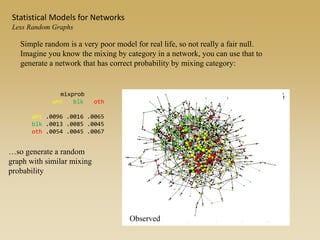
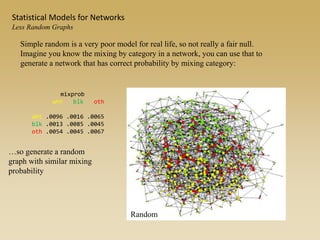
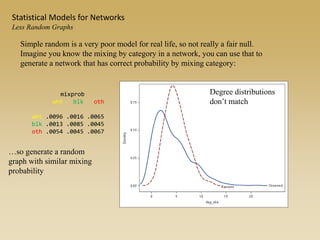
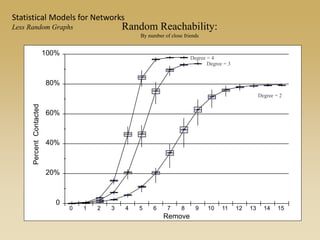
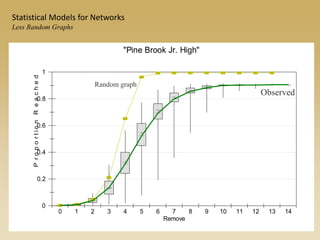
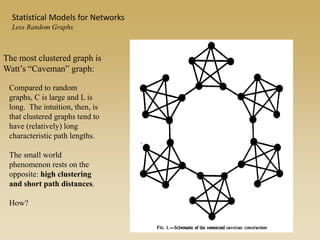
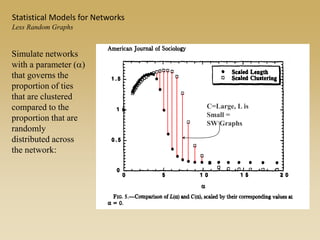
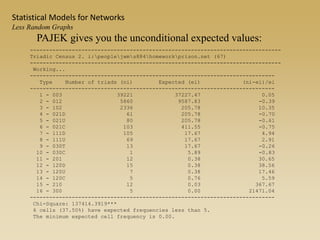
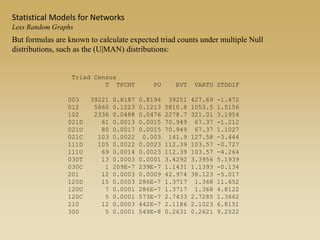
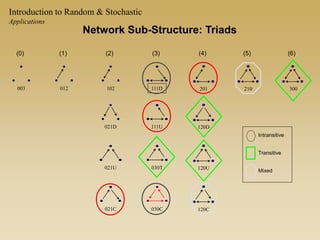
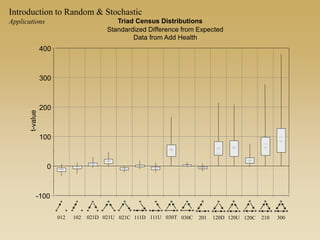
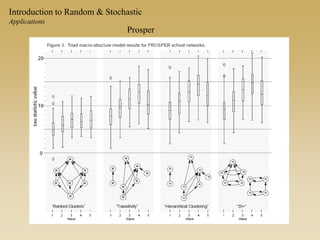
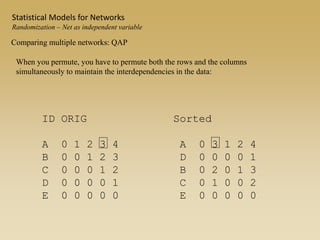
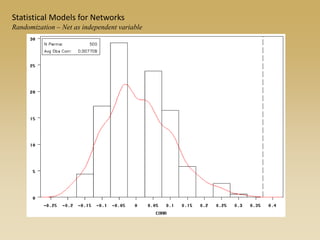
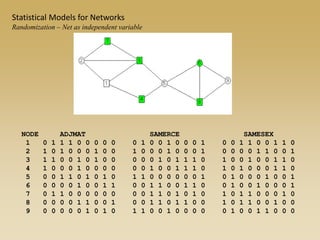
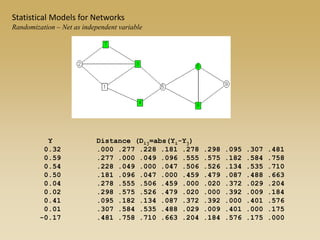
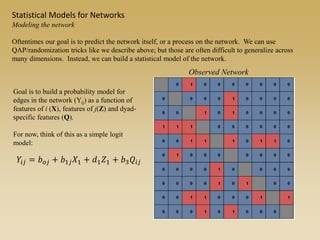
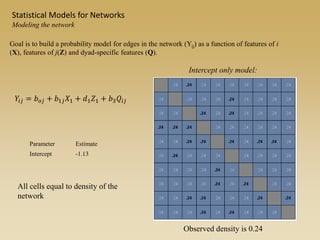
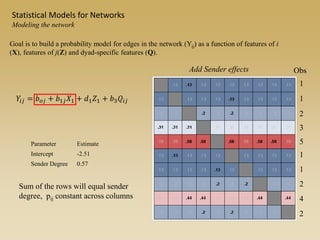
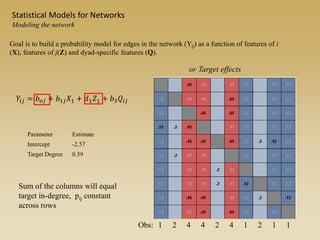
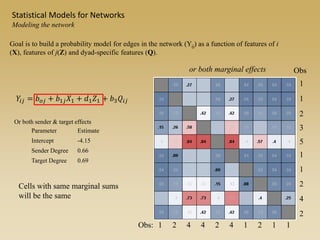
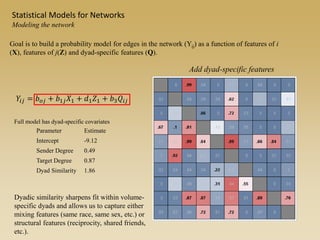
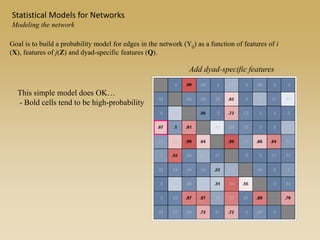
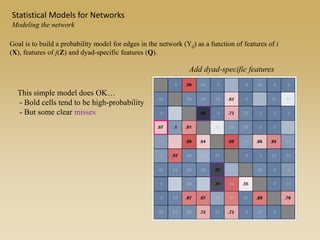
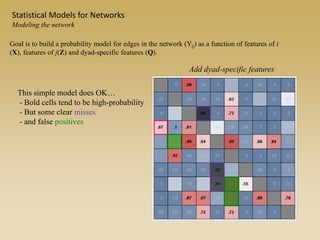
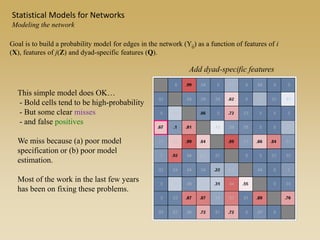
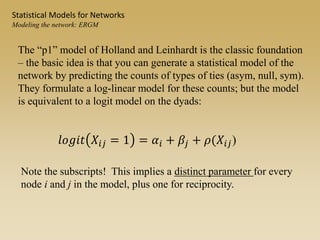
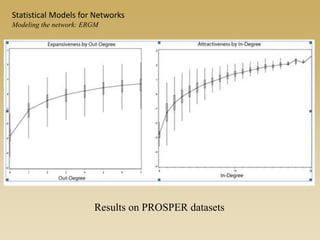
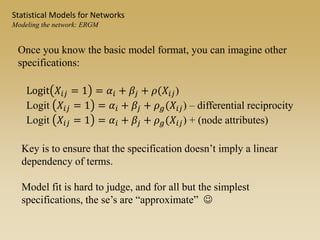
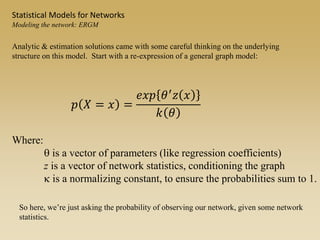
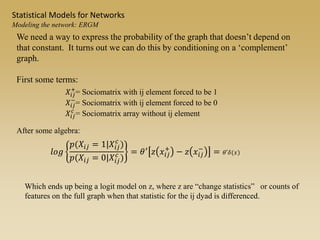
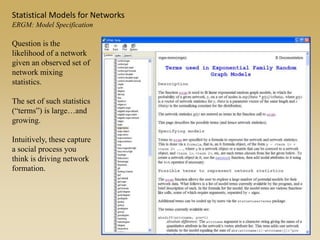
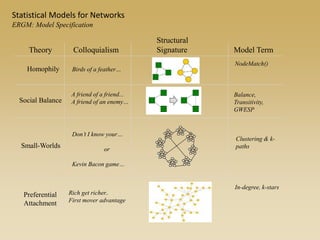
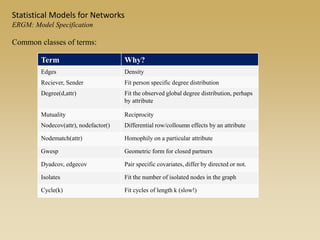
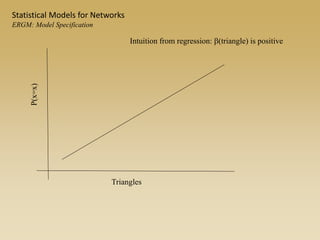
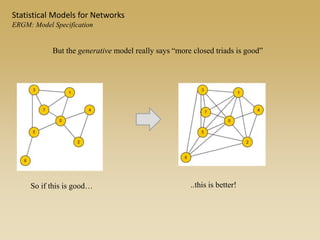
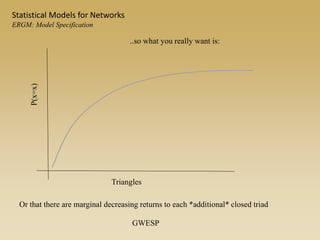
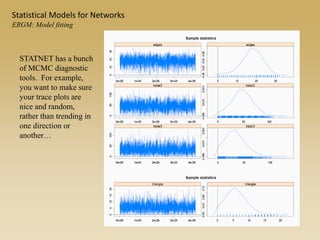
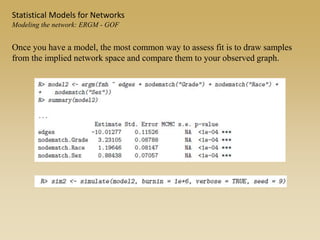
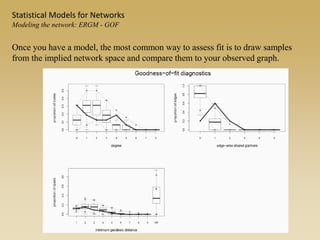
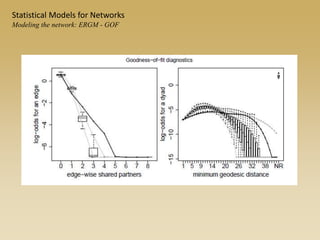
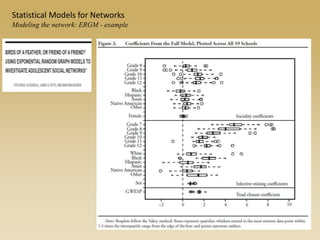
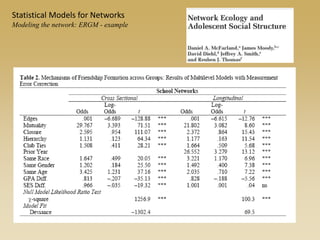
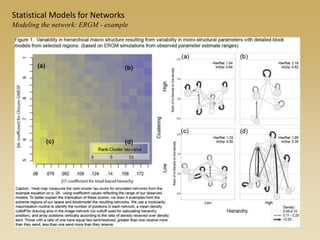
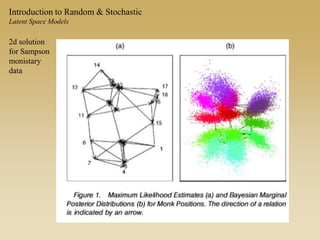
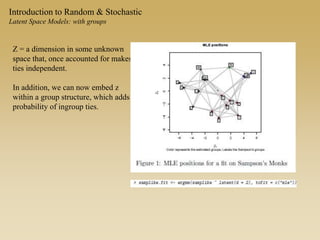
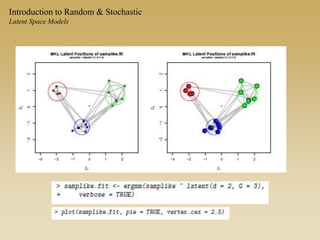
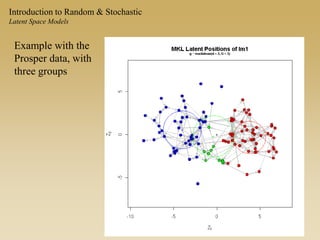
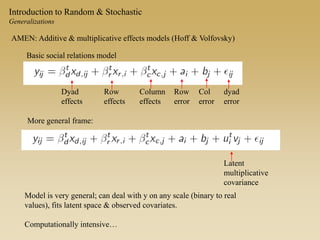
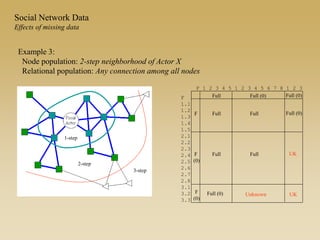
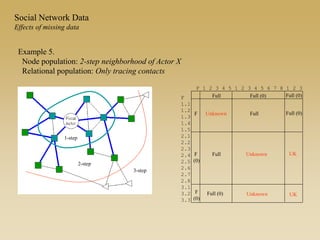
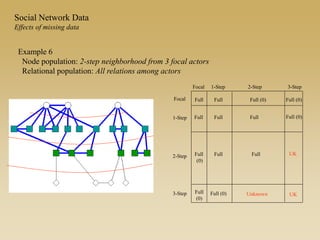
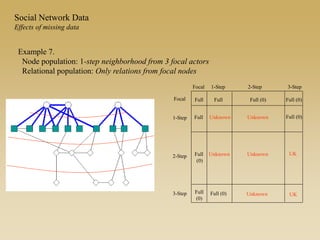
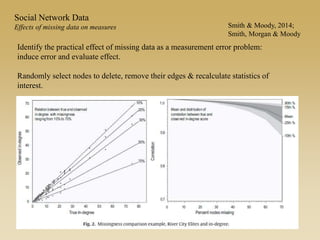
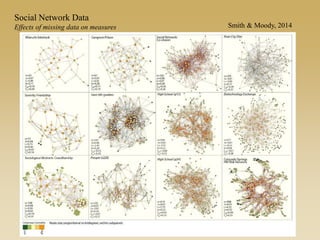
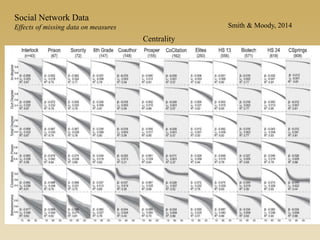
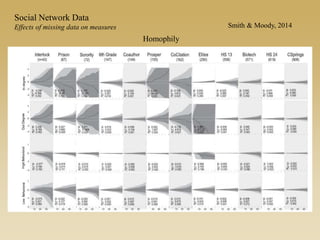
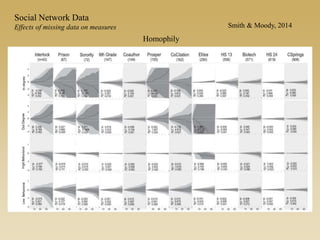
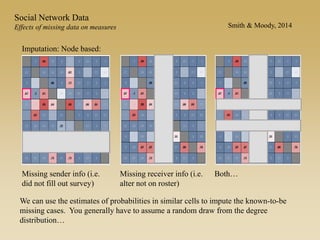
Statistical models for networks aim to compare observed networks to random graphs in order to assess statistical significance. Simple random graphs are commonly used as a baseline null model but are unrealistic. More developed null models condition on key network structures like degree distribution or mixing patterns to generate more reasonable random graphs for comparison. Network inference problems evaluate whether an observed network exhibits random or non-random properties relative to an appropriate null model.