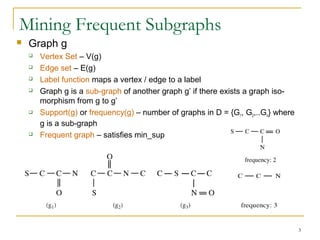
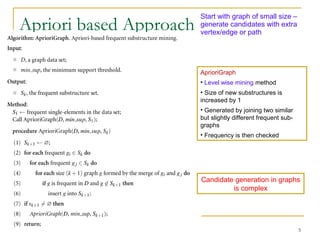
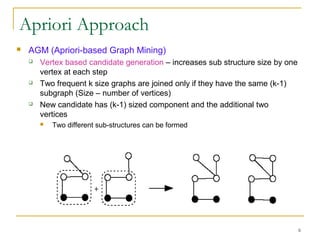
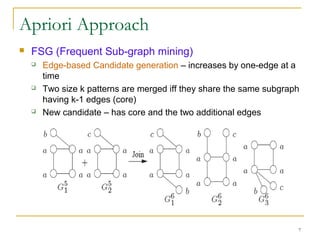
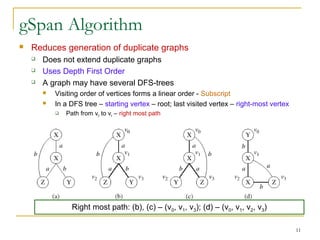
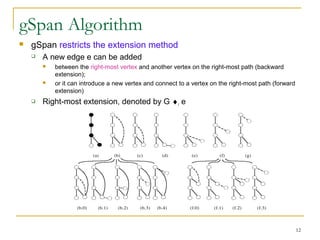
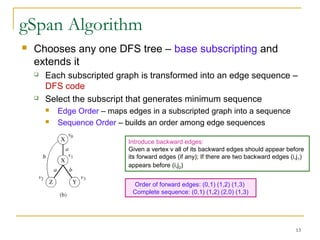
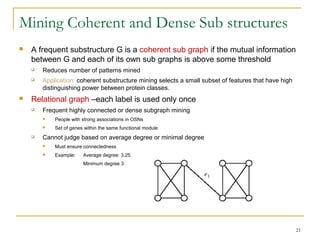
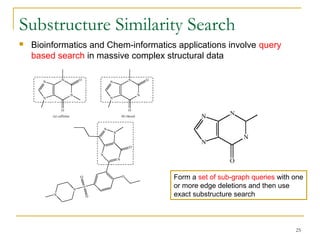
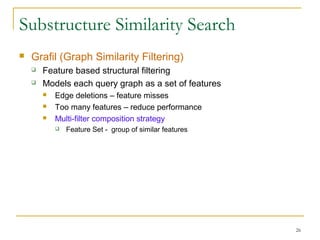
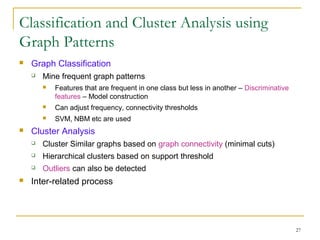
Graph mining involves discovering frequent subgraphs, patterns, or substructures from a graph database. It has applications in domains like cheminformatics, bioinformatics, social network analysis, and knowledge discovery. There are two main approaches for frequent subgraph mining - Apriori-based approaches that generate candidates level-wise and pattern growth approaches that extend frequent subgraphs. The gSpan algorithm reduces redundant searching by using a depth-first search ordering of the graphs. Mining closed, maximal or dense frequent subgraphs can further reduce the number of patterns discovered. Applications include graph indexing, substructure similarity search, and graph classification or clustering.