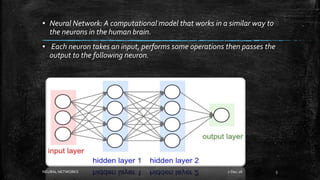
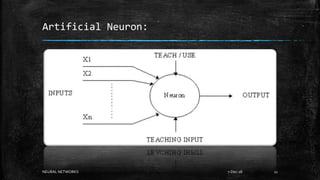
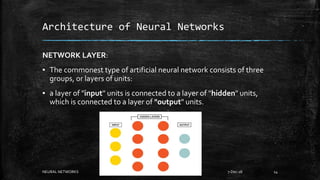
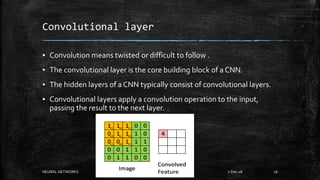
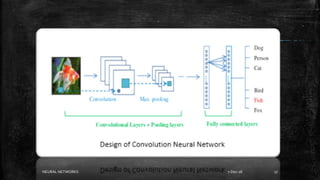
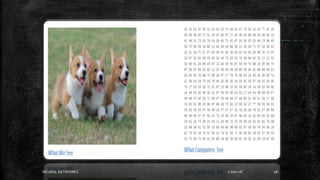
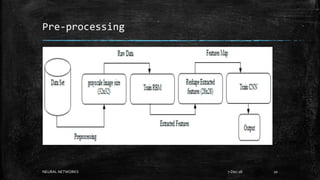
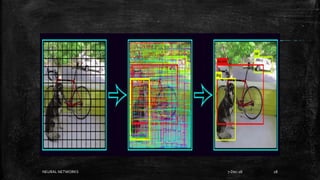
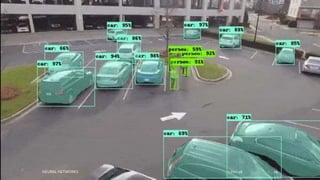
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes that process information using a principle called neural learning. The document discusses the history and evolution of neural networks. It also provides examples of applications like image recognition, medical diagnosis, and predictive analytics. Neural networks are well-suited for problems that are difficult to solve with traditional algorithms like pattern recognition and classification.