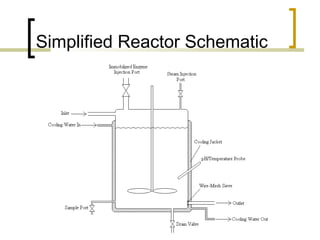
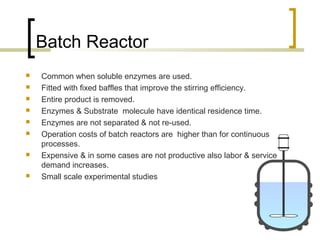
The document discusses immobilized enzyme reactors, categorizing them into batch and continuous types, highlighting their construction, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It details different types of reactors, such as stirred tank batch reactors and fluidized bed reactors, along with operational considerations for effective enzyme action. Additionally, specific examples of enzyme applications in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals are provided, emphasizing the importance of reactor selection based on characteristics like reactant viscosity and conversion efficiency.



![Batch reactor – Stirred tank [STR]
Simplest form..
Good mixing, ease of temperature & pH
control.
Loss of some enzyme activity may occur.
Modified form – Basket Reactor.
Basket reactor – enzymes are retained
over the impeller blades or baffles of the
tank reactor.
Both have a well mixed flow pattern.
High shear forces may damage cells.
Requires high energy input.
Application :- free & immobilized enzyme
reactions..
Recovery of products produced by
enzymes like lipase, glucose isomerase &
B-galactosidase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymereactor-161107064832/85/immobilized-Enzyme-reactors-batch-and-continuous-types-7-320.jpg)
![Batch reactor – Plug flow [PFR]
Alternative to flow pattern type of
reactors.
Flow rate controlled by a plug system.
Plug flow – Packed bed or Fluidized
bed
Used when inadequate product
formation in flow type reactors.
Advantage – external mass transfer
effects can be reduced by the
operational high fluid velocities.
Application :- used for obtaining
kinetic data on the reaction systems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymereactor-161107064832/85/immobilized-Enzyme-reactors-batch-and-continuous-types-8-320.jpg)
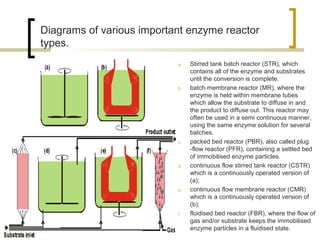
![Batch reactor – Packed-bed [PBR]
Modified form, Widely used.
When equipped with external
heating & cooling coils is also
called as PFR
Substrate stream flows at same
velocity, parallel to reactor with
no back-mixing.
3 substrate flow possibilities –
downward flow method, upward,
& recycling method.
Packed-bed reactors are used
with immobilized or particulate
biocatalysts.
Medium can be fed either at the
top or bottom & forms a
continuous liquid phase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymereactor-161107064832/85/immobilized-Enzyme-reactors-batch-and-continuous-types-9-320.jpg)
![Batch reactor – Fluidised-bed [FBR]
Intermediate between CSTRs & PBRs.
Consist of a bed of immobilized
enzymes which is fluidized by rapid
upwards flow of the substrate or in
combination with a gas or Secondary
liquid stream.
Fluidization requires large power input.
Heating & cooling coils are located
outwards.
Baffles are used to decrease stirring
efficiency.
Useful if the reaction involves the
utilization or release of gaseous
material.
Disadvantage – difficulty in scaling-up
these reactors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymereactor-161107064832/85/immobilized-Enzyme-reactors-batch-and-continuous-types-10-320.jpg)