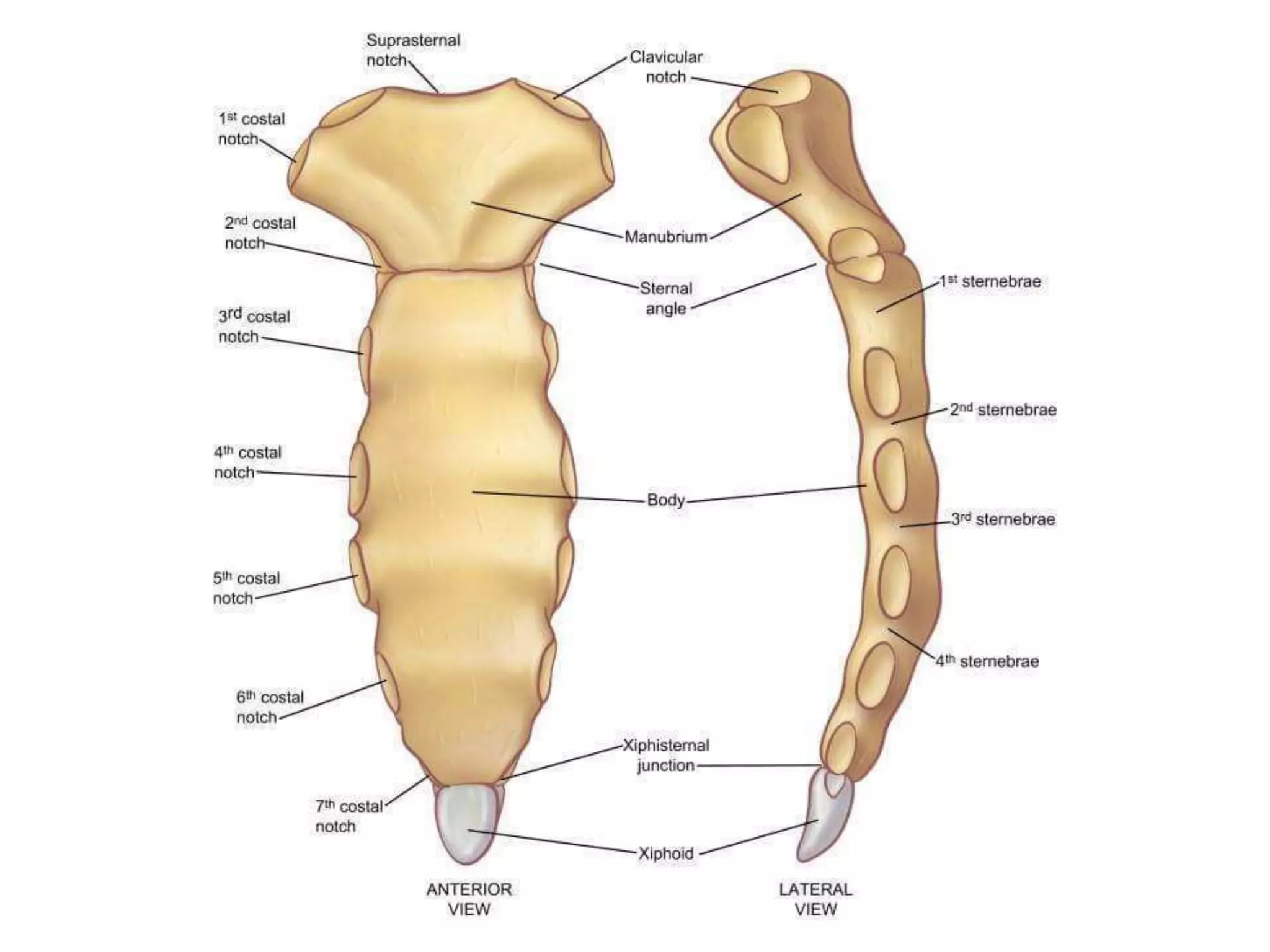
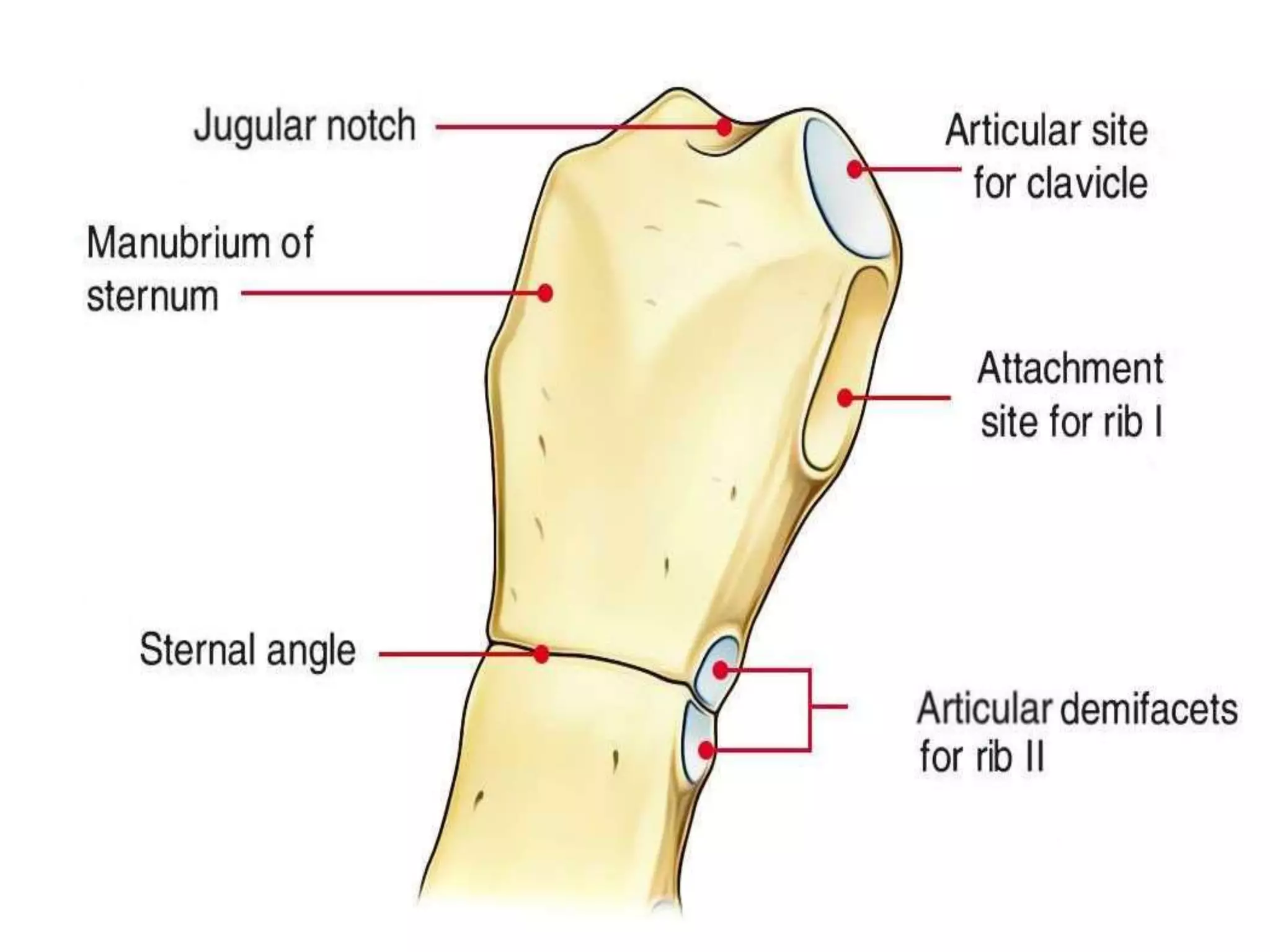
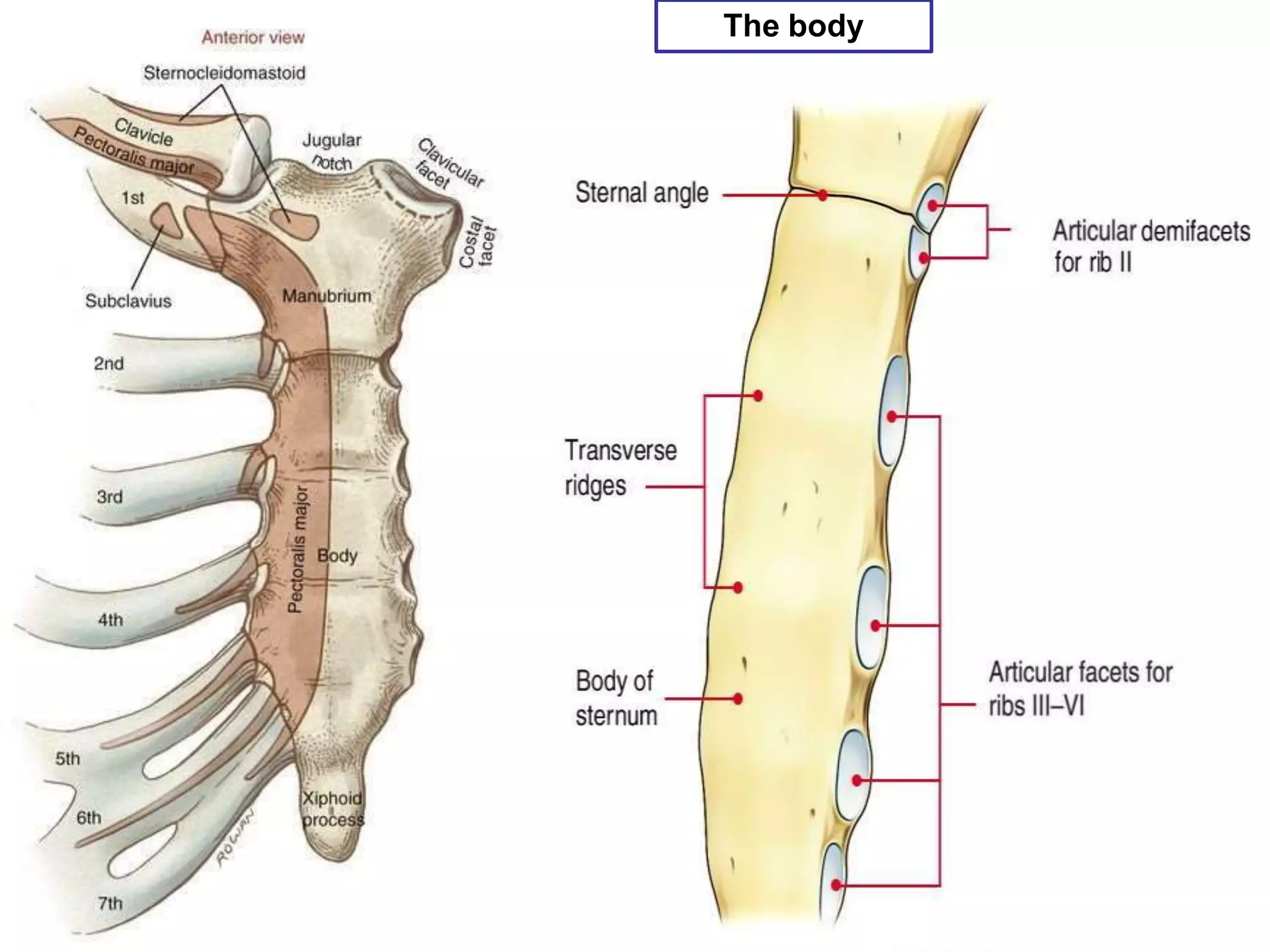
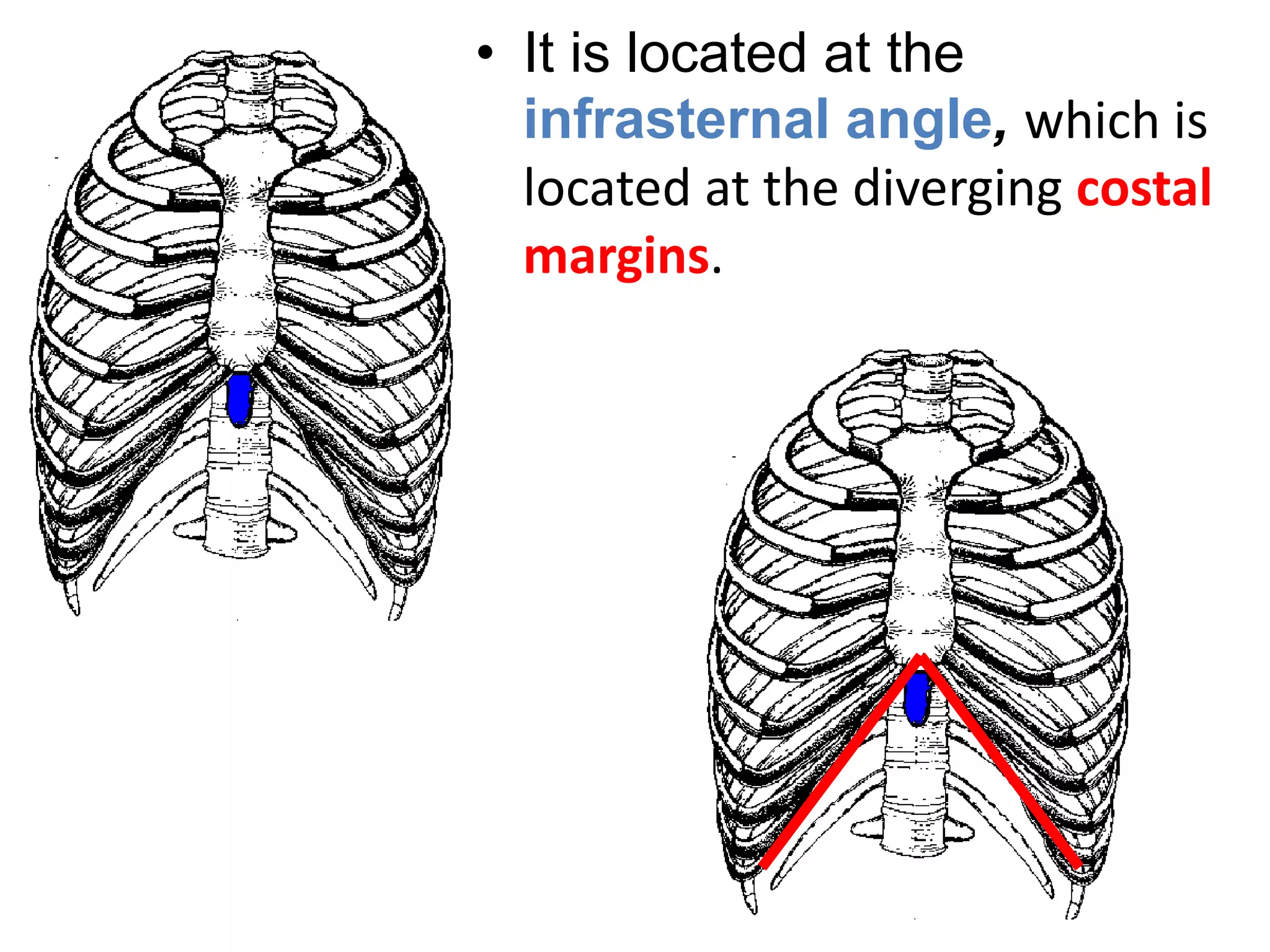
The thoracic cage is formed by the thoracic vertebrae, ribs, costal cartilages, and sternum. It protects the internal organs of the chest and supports the trunk. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. It articulates with the costal cartilages anteriorly and protects structures like the aorta posteriorly. Sternal fractures are common in car accidents and can cause serious internal bleeding if fragments are displaced.