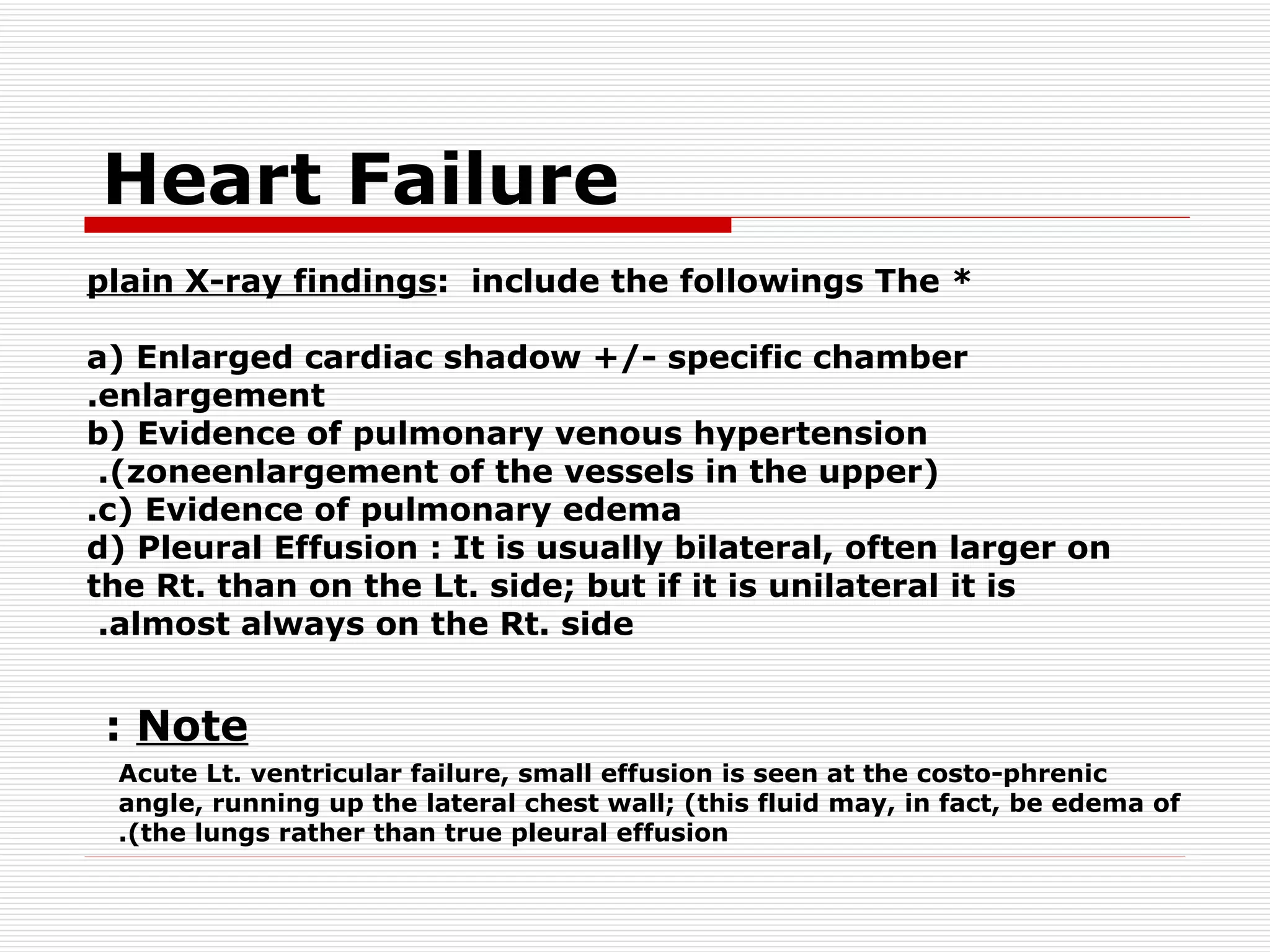
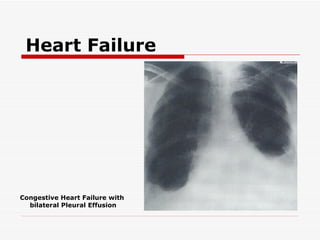
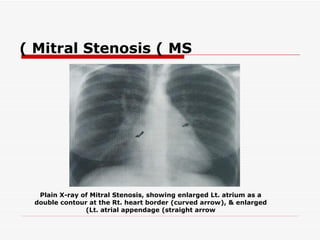
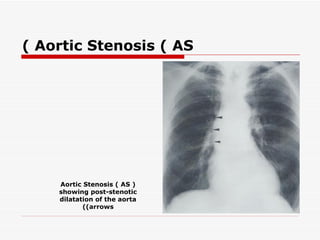
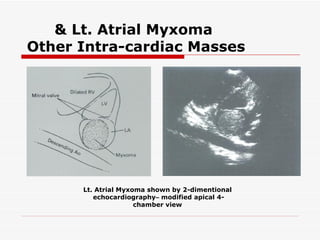
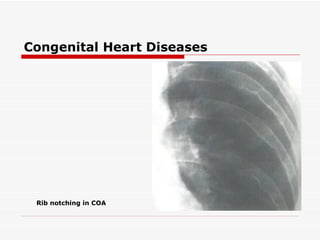
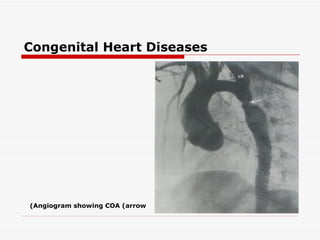
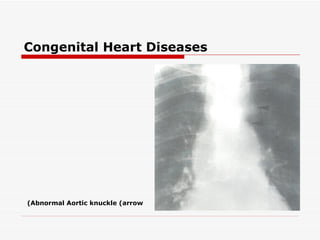
The document discusses various heart conditions and their appearances on plain X-rays. It describes findings including enlarged cardiac shadows, chamber enlargements, pulmonary edema, pleural effusions, valve calcifications, and post-stenotic vessel dilatations that indicate conditions such as mitral stenosis, mitral regurgitation, aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, congenital shunts, coarctation of the aorta, and tetralogy of Fallot. Intracardiac masses like left atrial myxomas are also addressed.