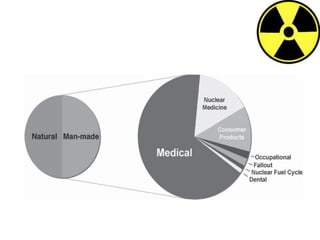
This document discusses radiation safety in dentistry. It covers the different sources of radiation, both natural and artificial. The key principles of radiation protection established by ICRP are justification, optimization, and dose limitation. The ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) principle should be followed to minimize unnecessary radiation exposure to patients and staff. Proper patient selection, examination techniques like collimation and filtration, use of protective barriers, and monitoring can help reduce radiation doses in dental radiography. Continuing education is important for staying up to date on radiation safety issues.












![• Source skin distance[SSD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiationprotection-220426135046/85/RADIATION-PROTECTION-pptx-15-320.jpg)



![• Use of PID’s[ Positioning indicating devices]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiationprotection-220426135046/85/RADIATION-PROTECTION-pptx-19-320.jpg)
![• Film holding devices [XCP-Holder]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiationprotection-220426135046/85/RADIATION-PROTECTION-pptx-20-320.jpg)

![LEAD APRON---
1/4THm mm [o.25mm] lead](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiationprotection-220426135046/85/RADIATION-PROTECTION-pptx-22-320.jpg)








![• Personnel-monitoring devices. Commonly referred to as film
badges.
• TLD [ Thermoluminescent dosimeter]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiationprotection-220426135046/85/RADIATION-PROTECTION-pptx-31-320.jpg)






