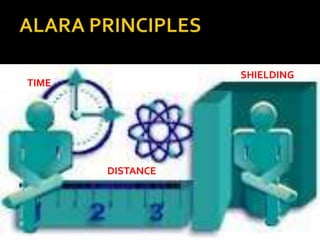
This document discusses radiation and its uses in medicine. It defines radiation as energy emitted in the form of particles or waves. Radiation is useful for medical imaging and treatment. It describes different types of radiation including electromagnetic radiation, alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and x-rays. It discusses how various medical imaging techniques like CT scans, x-rays, and mammograms expose patients to radiation, but ensure doses are kept as low as reasonably achievable. The document emphasizes principles of radiation safety for both patients and workers through justification of exposures, dose optimization and limitation.