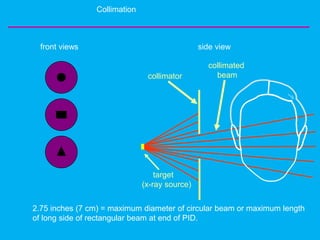
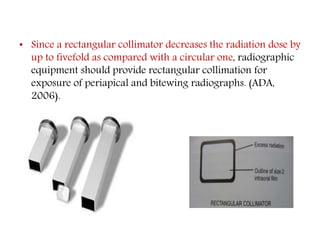
Radiation safety and protection measures are important to minimize radiation exposure for patients and dental staff. Early pioneers in dental radiography suffered health effects from excessive radiation doses. Radiation can come from natural sources like cosmic rays and radioactive elements in the ground, or man-made sources like medical imaging. Protection techniques include using thyroid collars and lead aprons for patients, fast film, rectangular collimation, and selecting proper exposure factors. Proper handling and processing of films is also needed to avoid retakes and reduce unnecessary radiation exposure.