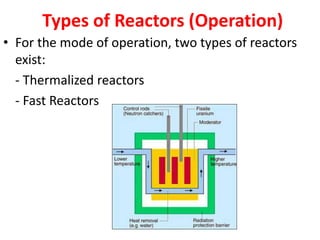
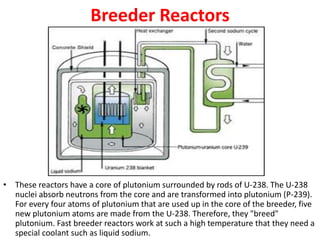
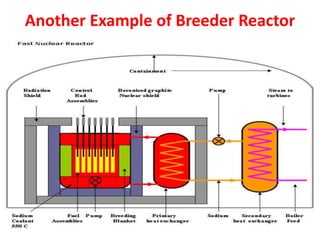
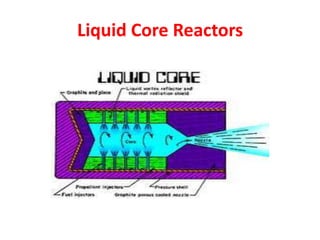
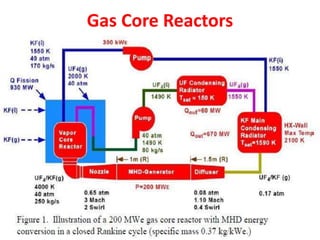
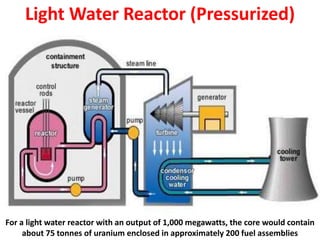
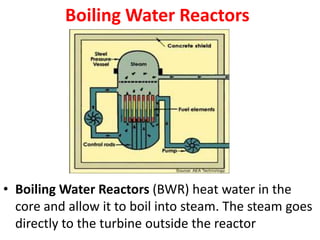
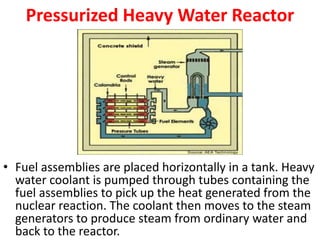
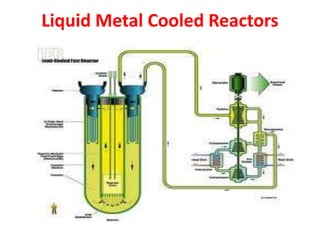
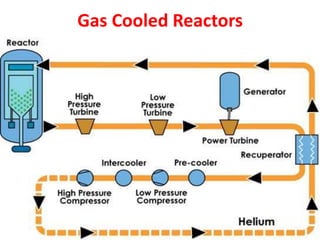
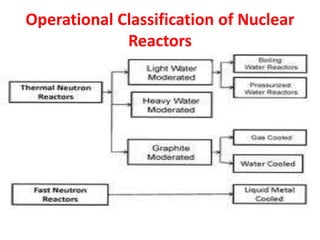
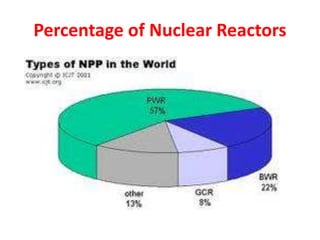
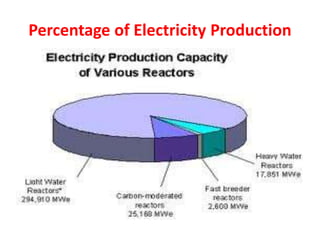
There are several types of nuclear reactors classified by their operation, purpose, fuel, and coolant. Reactors are either thermalized, which slow neutrons, or fast reactors. Their purpose can be power production, fuel conversion, breeding more fuel (breeder reactors), or research. Breeder reactors produce more fissile plutonium than they consume. Reactors also differ in whether they use solid, liquid, or gas fuels and water, heavy water, liquid metals like sodium, or gases like carbon dioxide as coolants. The most common reactor types are light water reactors (using regular water), boiling water reactors, and pressurized heavy water reactors.