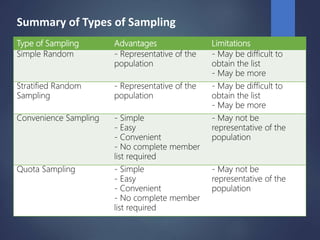
This document discusses different sampling techniques used in research. It defines key terms like population, sample, and element. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling and stratified random sampling, as well as non-probability methods like convenience sampling and quota sampling. For each method, it provides details on the steps involved and discusses their advantages and limitations for representing a population. The goal of sampling is to select participants in a way that allows results to be generalized to the larger population from which the sample was drawn.