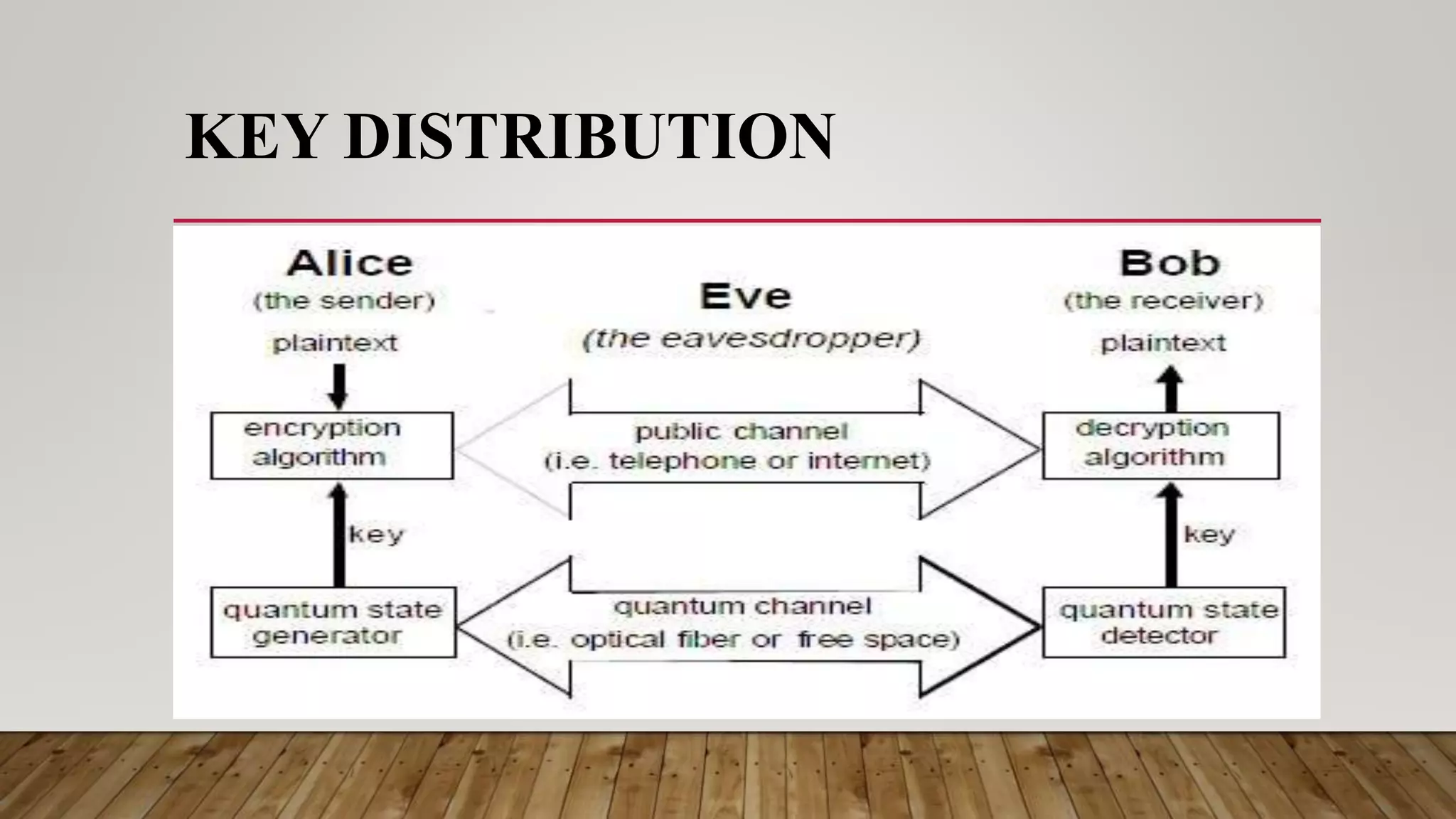
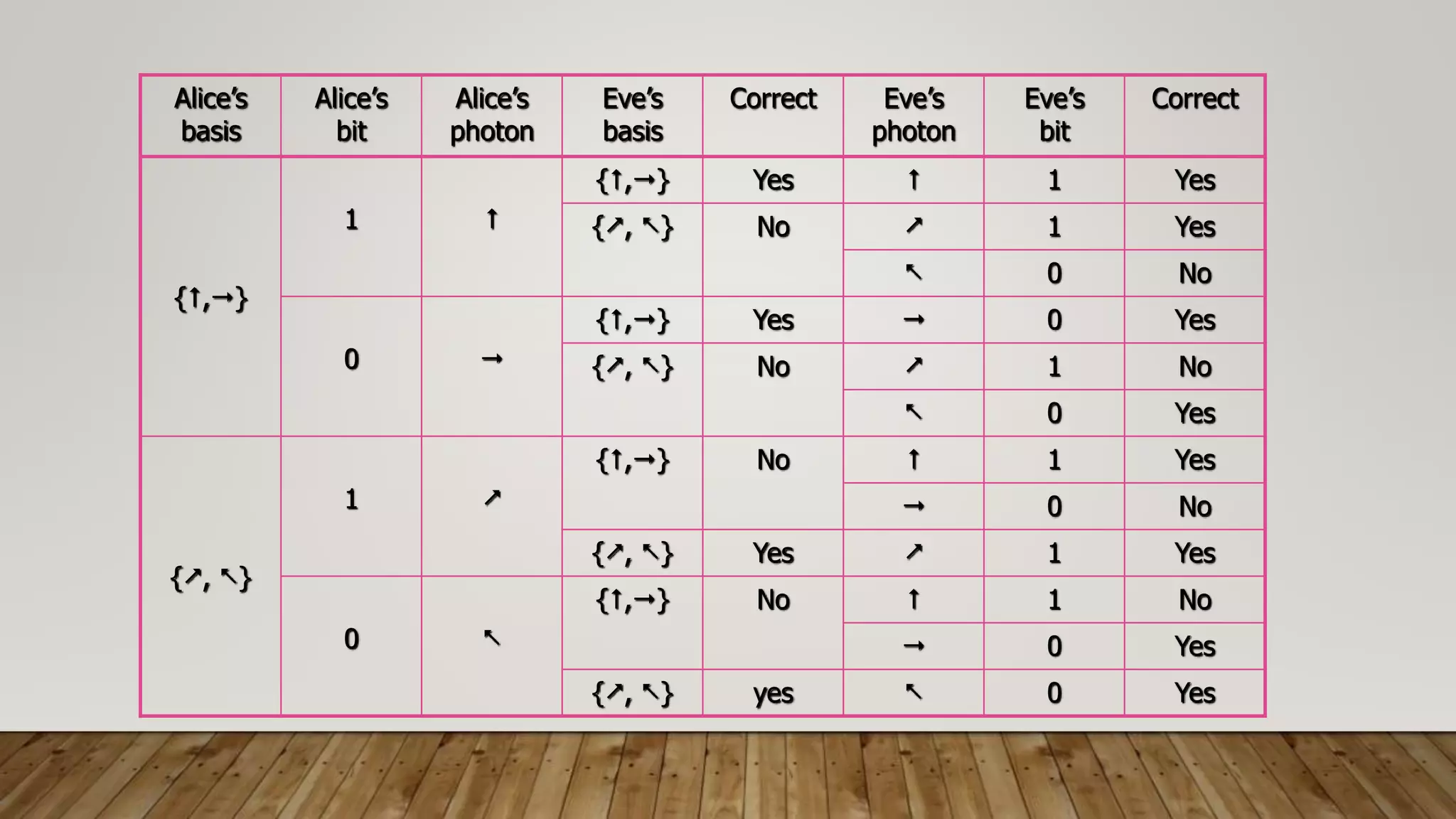
This document discusses the principles and history of quantum cryptography. It explains that quantum cryptography uses the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and quantum entanglement to securely transmit encryption keys. It outlines the key distribution process where Alice and Bob send polarized photons in random bases and later reveal the bases to determine the shared key. The document also discusses how an eavesdropper like Eve would not be able to intercept the photons without introducing errors, and how Alice and Bob can detect errors during transmission.