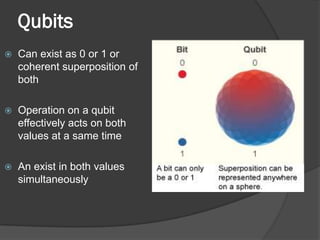
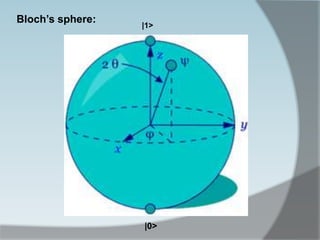
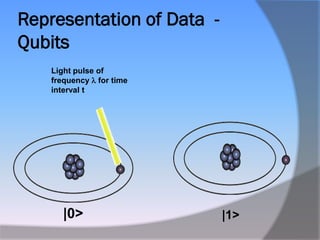
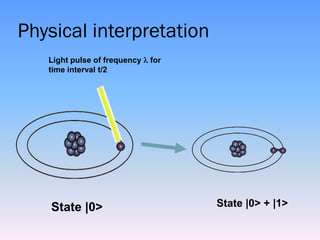
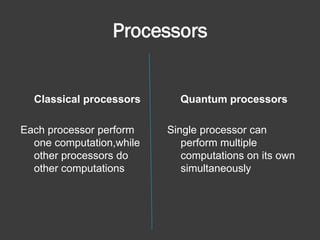
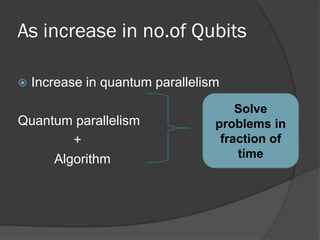
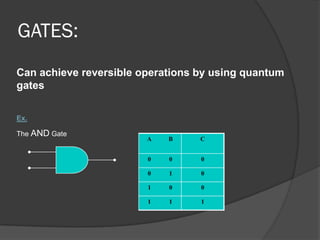
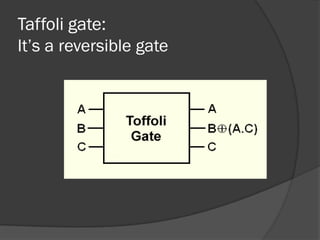
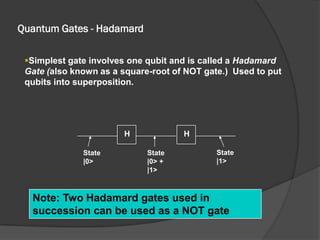
The document discusses quantum computing, emphasizing its reliance on qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, unlike classical bits. It highlights the advantages of quantum computers, such as significantly faster processing times for complex calculations, exemplified by Shor's algorithm for factoring large numbers. Additionally, it addresses the necessity for novel technologies, such as nanotechnology, to create these advanced computational systems.