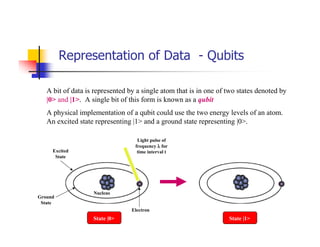
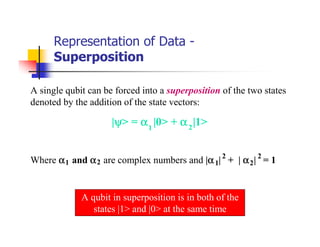
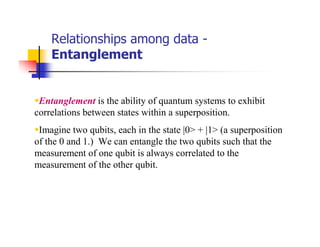
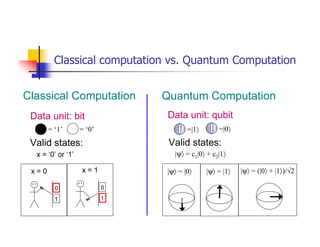
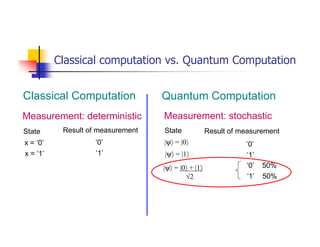
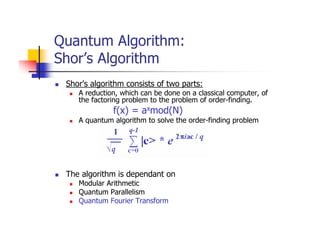
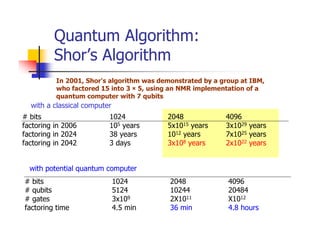
Quantum computing uses quantum mechanics phenomena like superposition and entanglement to perform operations on quantum bits (qubits) and solve certain problems much faster than classical computers. One such problem is integer factorization, for which Peter Shor devised an algorithm in 1994 that a quantum computer could solve much more efficiently than classical computers. While quantum computing is still in development, it has the potential to break popular encryption systems like RSA and simulate quantum systems. Practical implementations of quantum computing include ion traps, NMR, optical photons, and solid-state approaches. Quantum computing could enable applications in encryption-breaking, simulation, and cryptography, among other areas.