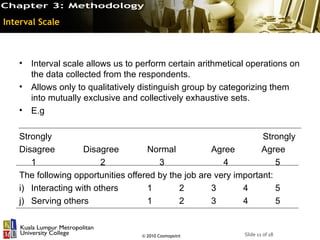
The document discusses research design and methodology. It explains that a research design is a framework that specifies the procedures needed to address a business problem. A good research design ensures the information collected is relevant, necessary information is obtained, and the project is conducted efficiently. It also discusses theoretical frameworks, variables, scales of measurement for variables, and common scaling techniques.