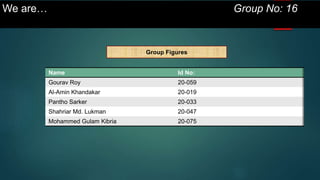
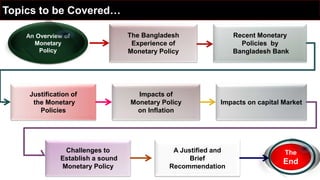
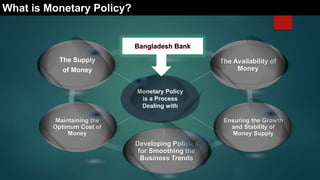
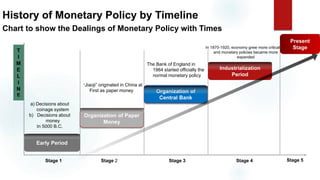
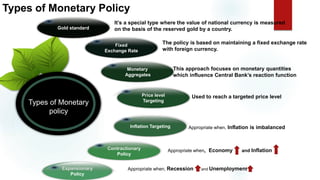
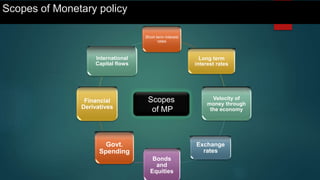
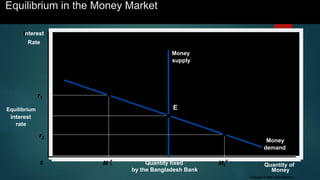
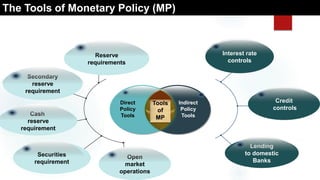
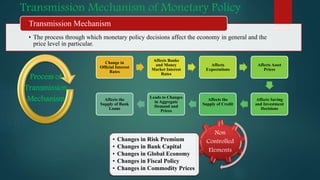
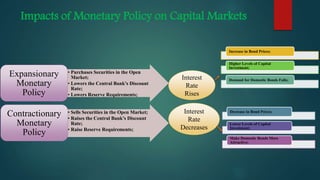
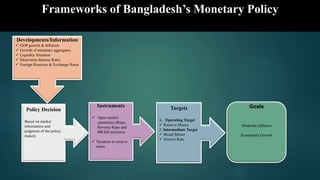
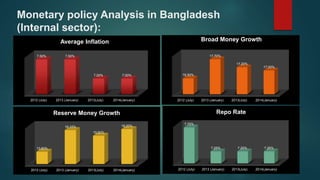
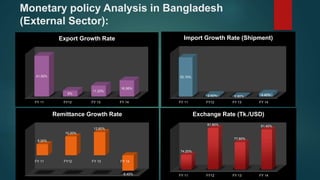
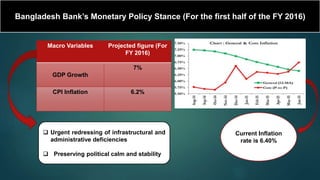
This document is a presentation on monetary policy in Bangladesh by Group 16. It begins with introductions of the group members. The presentation covers topics such as the definition of monetary policy, the tools and transmission mechanisms of monetary policy, impacts of monetary policy on inflation and capital markets, Bangladesh Bank's monetary policy stances and challenges to monetary policy in Bangladesh. The presentation provides an overview of key concepts in monetary policy as well as analysis of monetary policies implemented in Bangladesh.