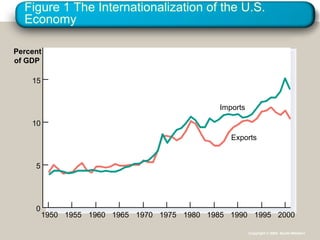
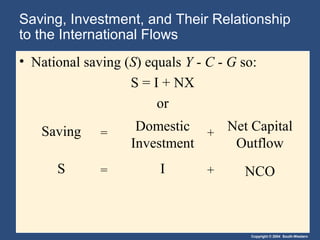
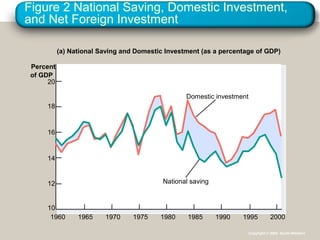
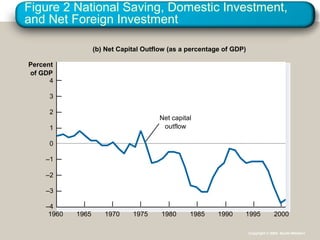
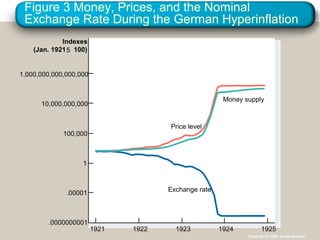
This document provides an overview of key concepts in open-economy macroeconomics. It defines open and closed economies, and describes how an open economy interacts through international trade and financial flows. It explains exports, imports, the trade balance, and factors that influence them. It also discusses net capital flows, interest rates, and the relationship between saving, investment, and international flows. Finally, it introduces nominal and real exchange rates, and the theory of purchasing power parity.