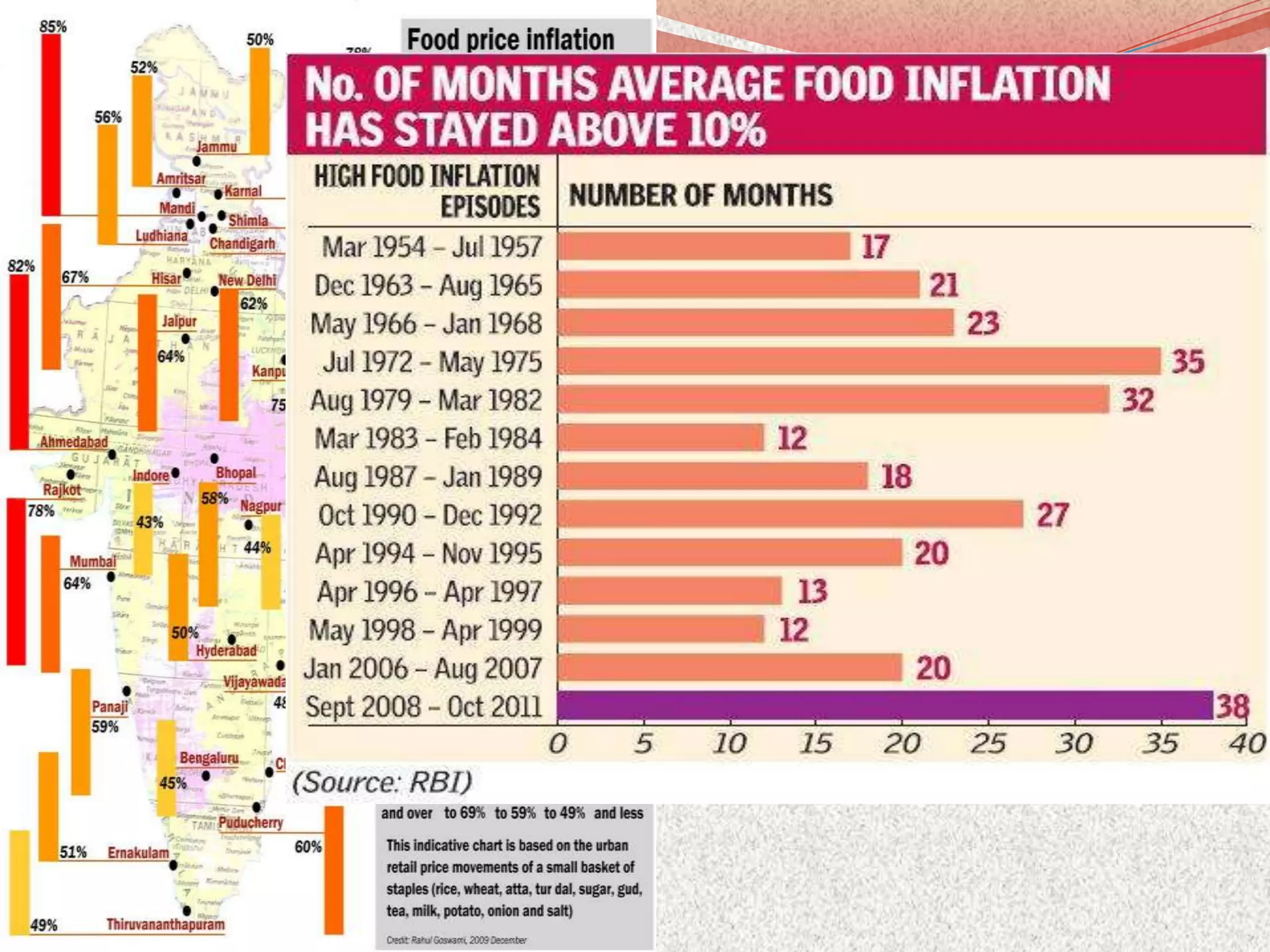
This document discusses inflation, its causes and effects. It defines inflation as a general rise in price levels over time which erodes purchasing power. Inflation is caused by excess money supply chasing limited goods. Key effects are a changing income distribution, reduced savings and capital formation, profits from price rises leading to black markets, and hardship for those on fixed incomes. While some argue low inflation spurs growth, critics say it ultimately hinders growth. The document examines India's anti-inflation measures and policies to better control inflation like monetary and fiscal policies, wage limits, spending cuts, and supply-side reforms.