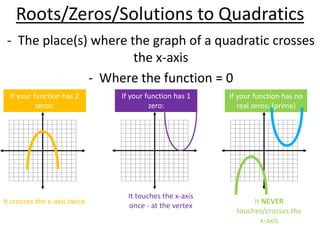
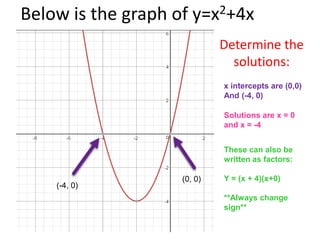
This document discusses key properties of quadratic graphs and functions including:
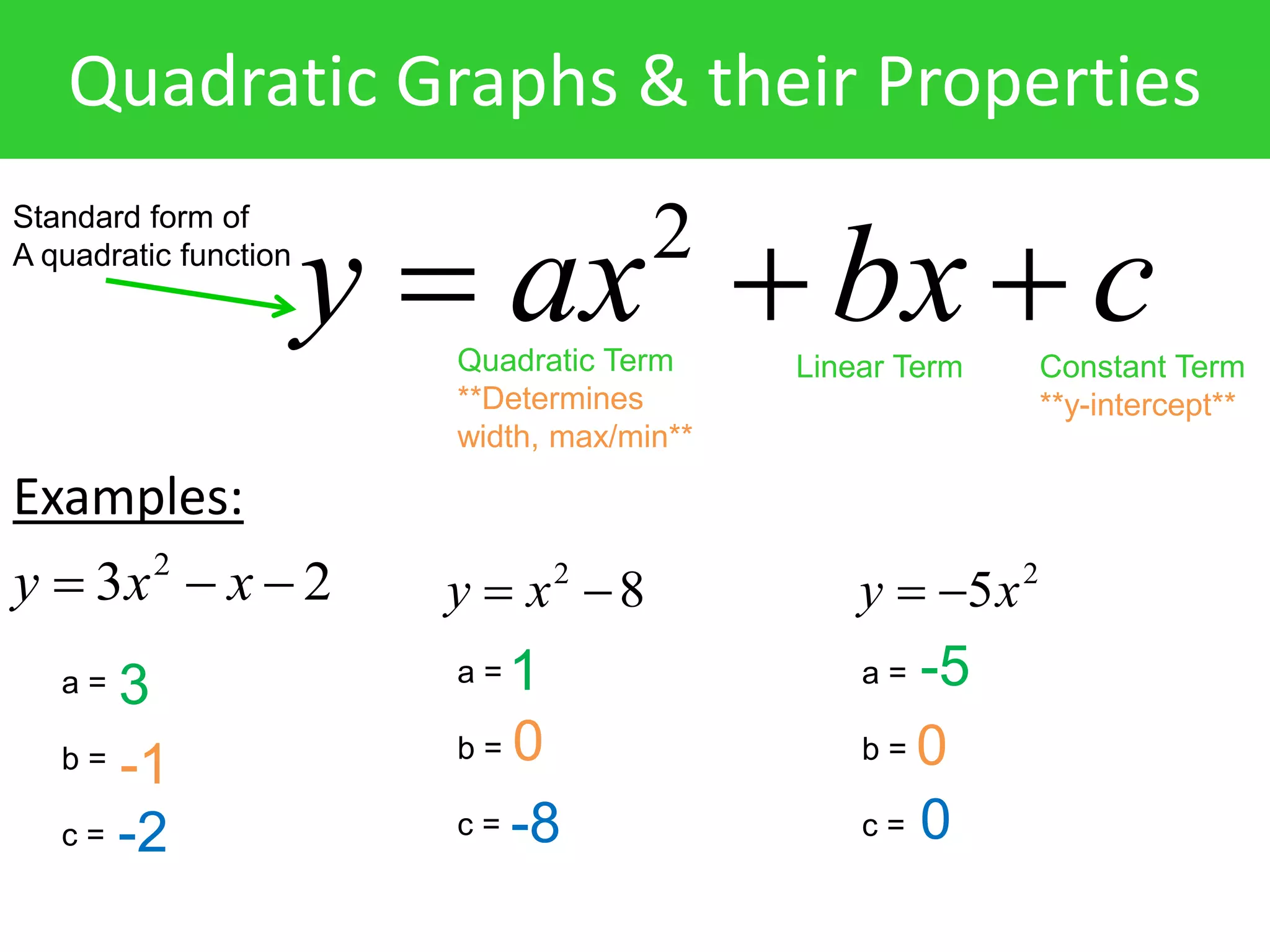
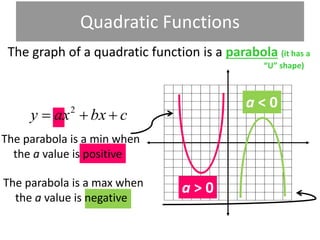
1) The standard form of a quadratic function is ax^2 + bx + c. The a value determines the width and whether there is a maximum or minimum.
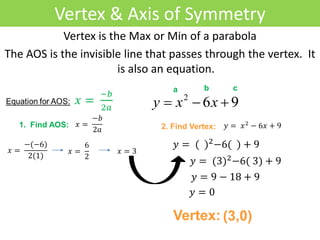
2) The vertex is the maximum or minimum point, which can be found using the formula x = -b/2a.
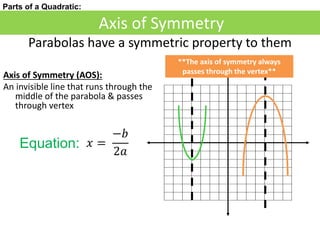
3) The axis of symmetry is the line that passes through the vertex and the parabola is symmetric about this line. The axis of symmetry is defined by the equation x = -b/2a.