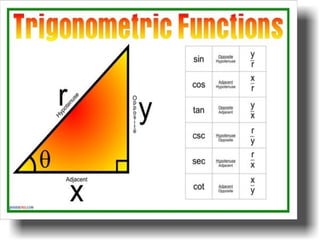
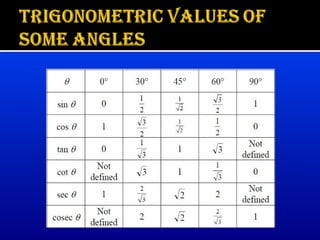
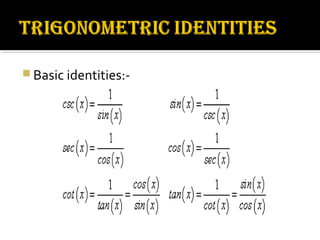
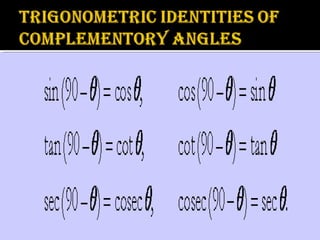
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships involving lengths and angles of triangles. It emerged during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomy. Hipparchus is considered the founder of trigonometry, compiling the first trigonometric table in the 2nd century BC. Key trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent were discovered between the 5th-10th centuries CE by mathematicians including Aryabhata, Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, and Abu al-Wafa. Trigonometry is applied to calculate angles of elevation and depression used in applications like determining the angle an airplane is viewed from the ground.