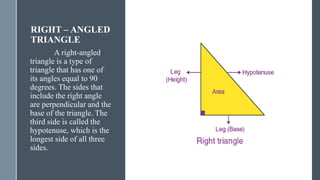
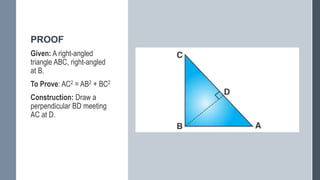
The document explains Pythagoras theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. It provides the definition of a right-angled triangle, the formula for the theorem, and a proof of the theorem. It also discusses applications of the theorem such as determining if a triangle is right-angled or calculating an unknown side of a right triangle.