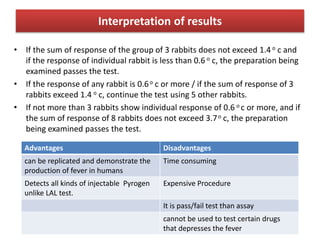
This document summarizes information about pyrogens and pyrogenicity. It defines pyrogens as agents that cause an increase in body temperature when injected. The most common pyrogens in pharmaceuticals are bacterial endotoxins from gram-negative bacteria. There are two classes of pyrogens - endogenous pyrogens produced within the body and exogenous pyrogens from external sources. Common sources of pyrogens in pharmaceutical products include water, materials, and equipment. The rabbit pyrogen test involves injecting a substance into rabbits and measuring temperature changes, while the LAL test detects endotoxins using lysate from horseshoe crab blood.