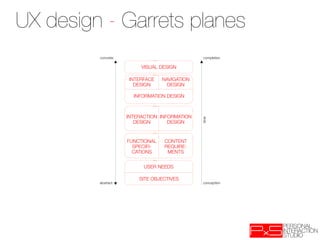
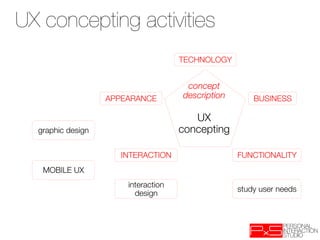
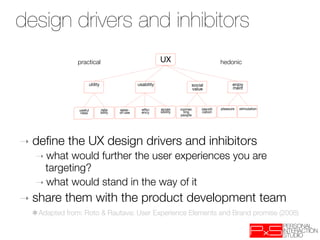
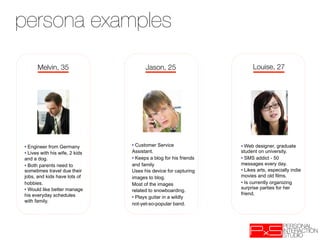
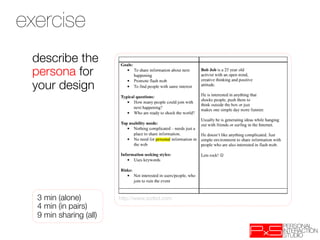
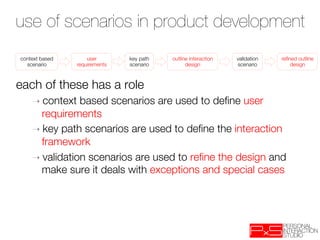
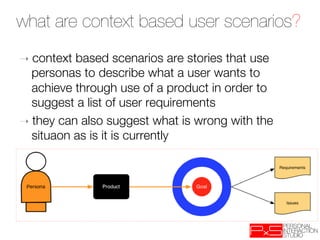
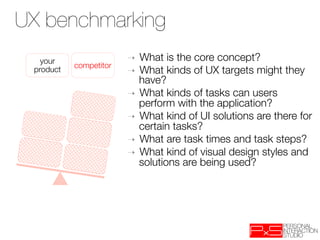
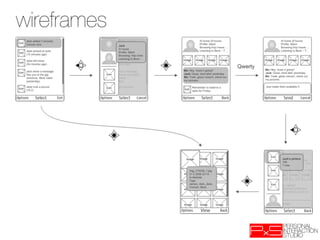
This document provides an overview of UX design techniques taught in a course at EPFL in spring 2012. It discusses conducting interviews to gather initial feedback, creating personas to represent user segments, developing scenarios to illustrate how personas would interact with a system, and using concepts, storyboards and prototypes at varying levels of detail to visualize and validate ideas early in the design process. The goal of concepting is to help manage risks by discovering if an idea is not viable before significant resources are invested in development.