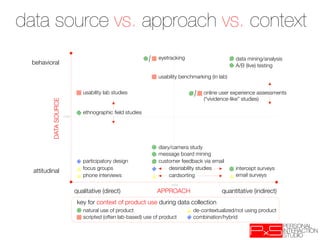
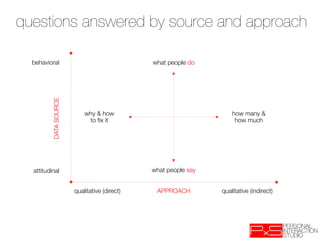
The document provides an overview of qualitative analysis techniques for gathering user insights including:
- Brainstorming, competitive analysis, literature research, and interviews to generate ideas
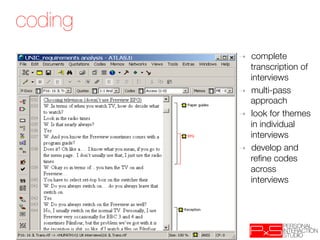
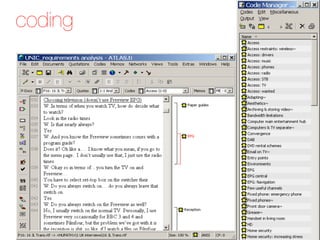
- Coding interview transcripts to group similar responses and surface themes across participants
- Approaches like interpretative techniques, recursive abstraction, and content analysis to analyze qualitative data
It also describes coding as assigning summaries of responses to groups to facilitate comparison and discussing coding as either an in-depth, multi-pass process or a quicker approach akin to card sorting.