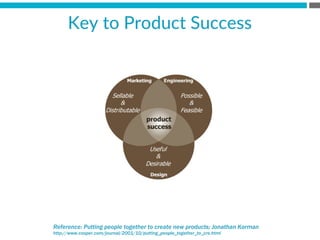
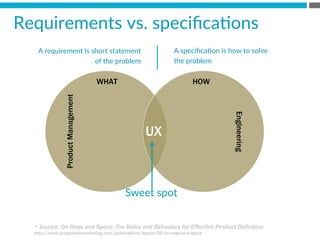
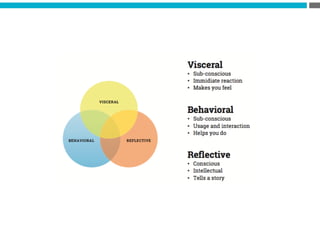
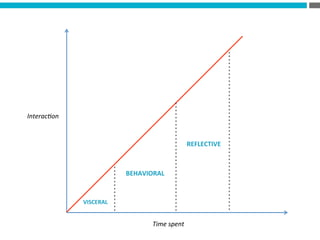
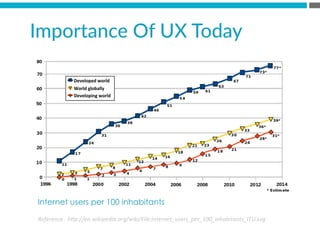
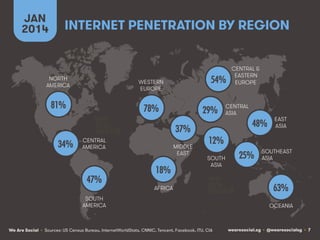
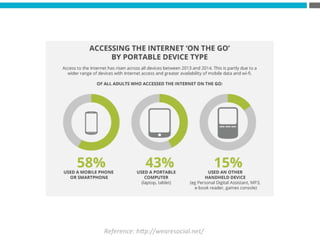
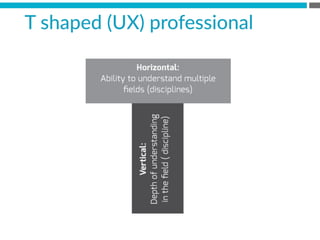
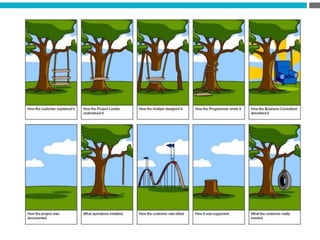
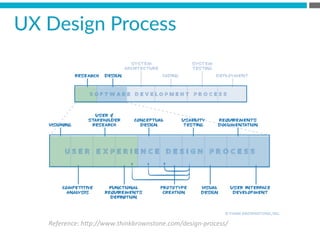
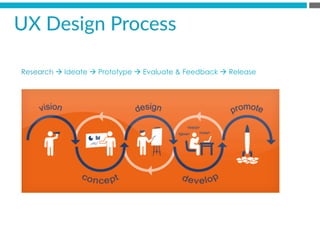
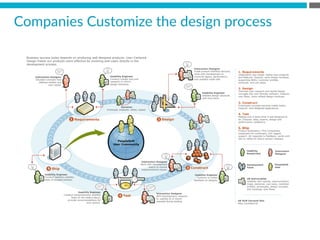
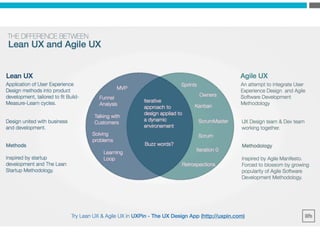
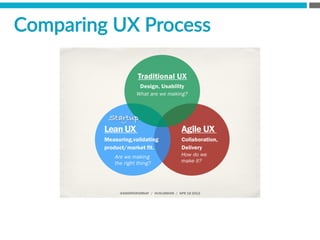
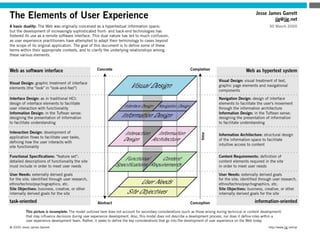
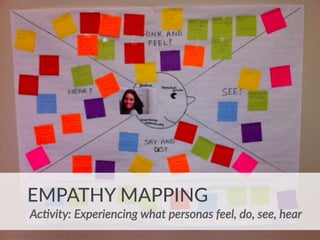
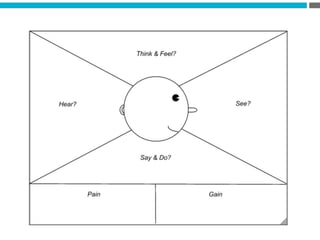
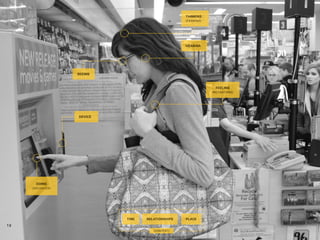
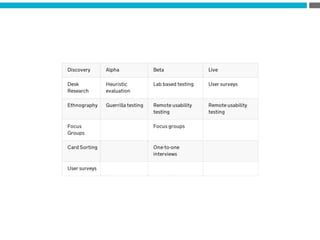
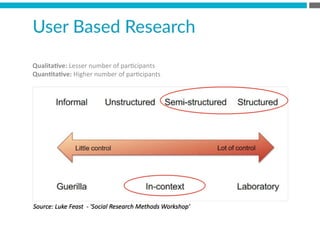
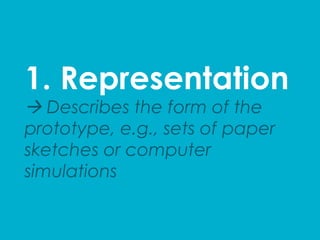
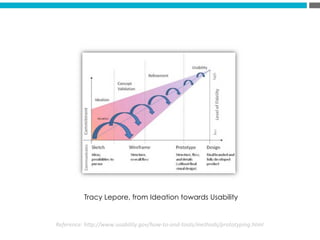
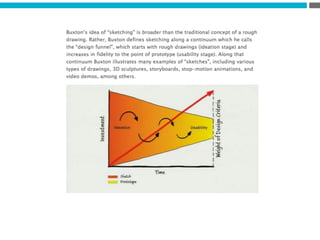
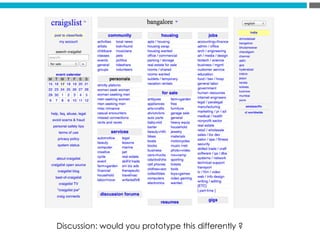
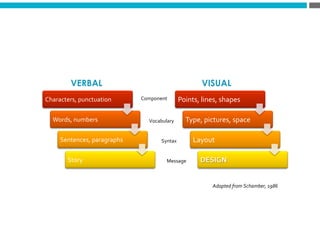
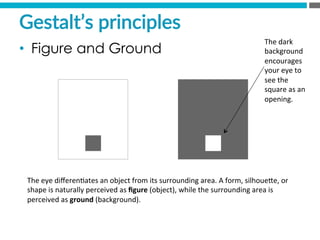
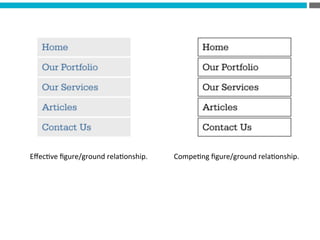
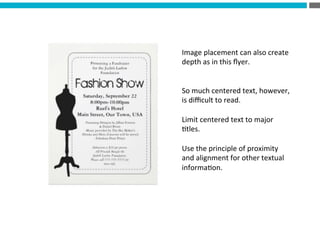
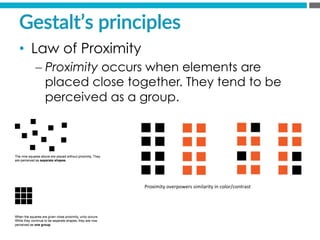
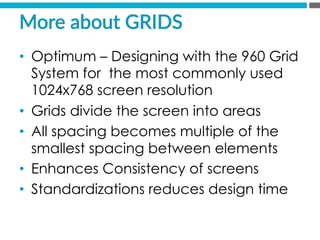
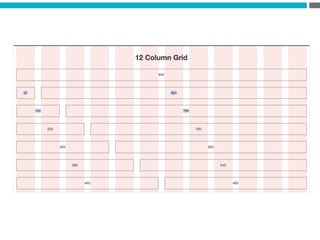
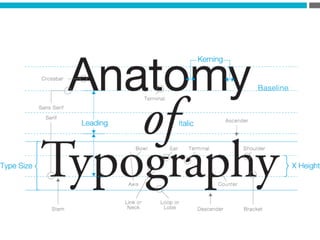
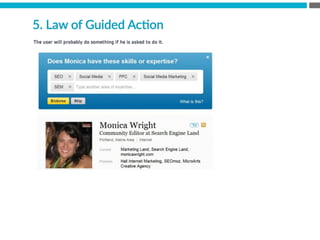
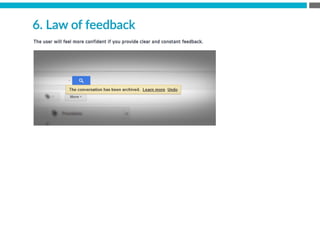
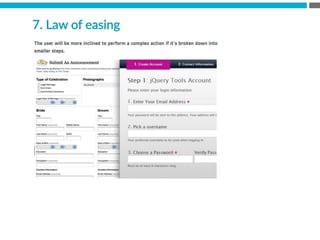
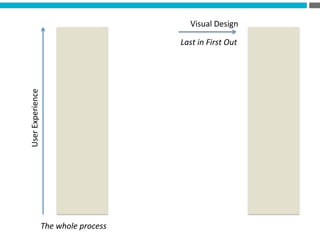
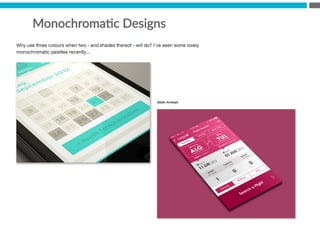
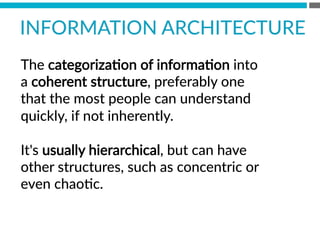
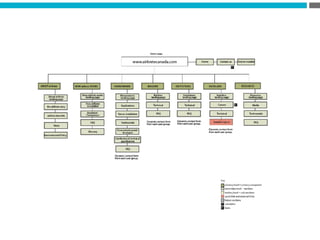
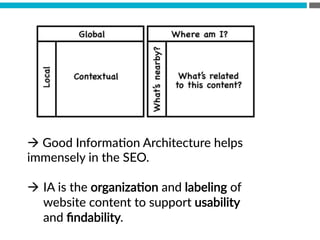
The document provides an introduction to KshiBz Anand, a professor of design and founder of several design consultancies. It summarizes his background and experience, including past roles at Motorola, Infosys, and other companies. It also lists his education, including an MS in HCI Design from Indiana University and a BDes in Communication Design from IIT Guwahati. Contact information is provided at the end.