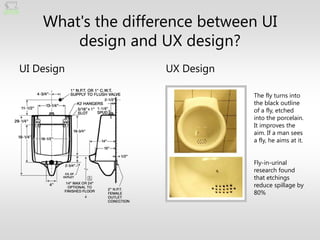
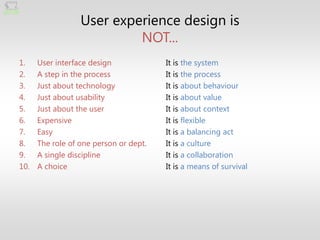
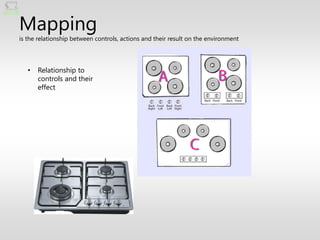
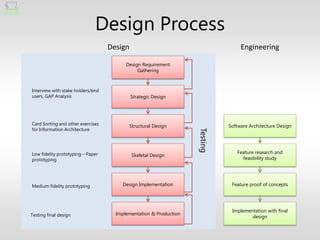
The document discusses the fundamentals of user experience (UX) design, emphasizing that it is a holistic and collaborative process rather than just a user interface (UI) element or a single activity. It outlines key design principles and the importance of integrating UX design into organizational culture to enhance user interactions across various platforms. Ultimately, effective UX design is portrayed as essential for survival in today’s complex design landscape.