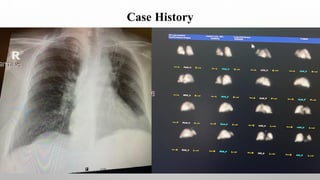
This document summarizes a pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan that was performed on an 80-year-old female patient with a history of hypertension and newly diagnosed Burkett's lymphoma. The scan involved nuclear medicine tests to evaluate lung ventilation and perfusion. The findings showed a heterogeneous pattern of tracer distribution in the left lung with multiple matched defects seen on both the perfusion and ventilation scans, suggesting a pulmonary embolism. The conclusion was that the scan results were consistent with the patient's current symptoms of potential pulmonary embolism.