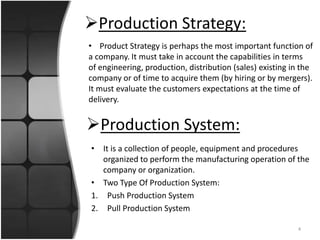
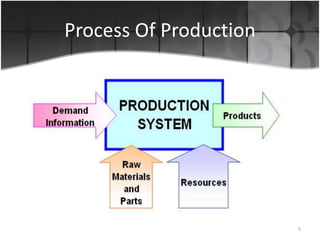
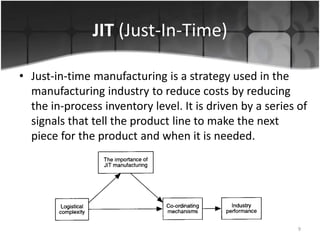
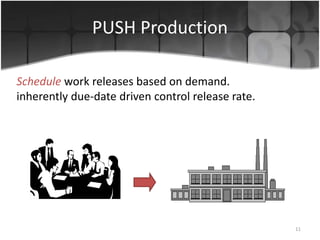
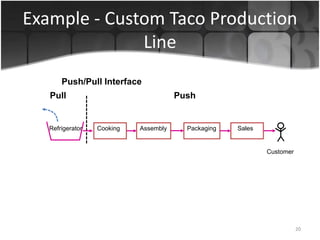
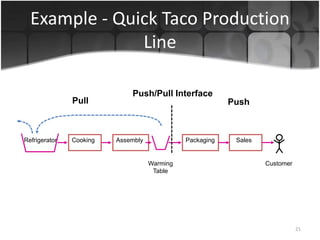
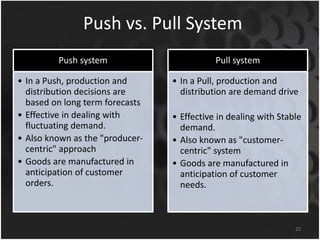
The document provides an overview of production systems, outlining key concepts such as Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing. It contrasts push and pull production systems, detailing their advantages and disadvantages, along with examples of each. The document emphasizes the importance of aligning production strategies with customer demands and operational capabilities.