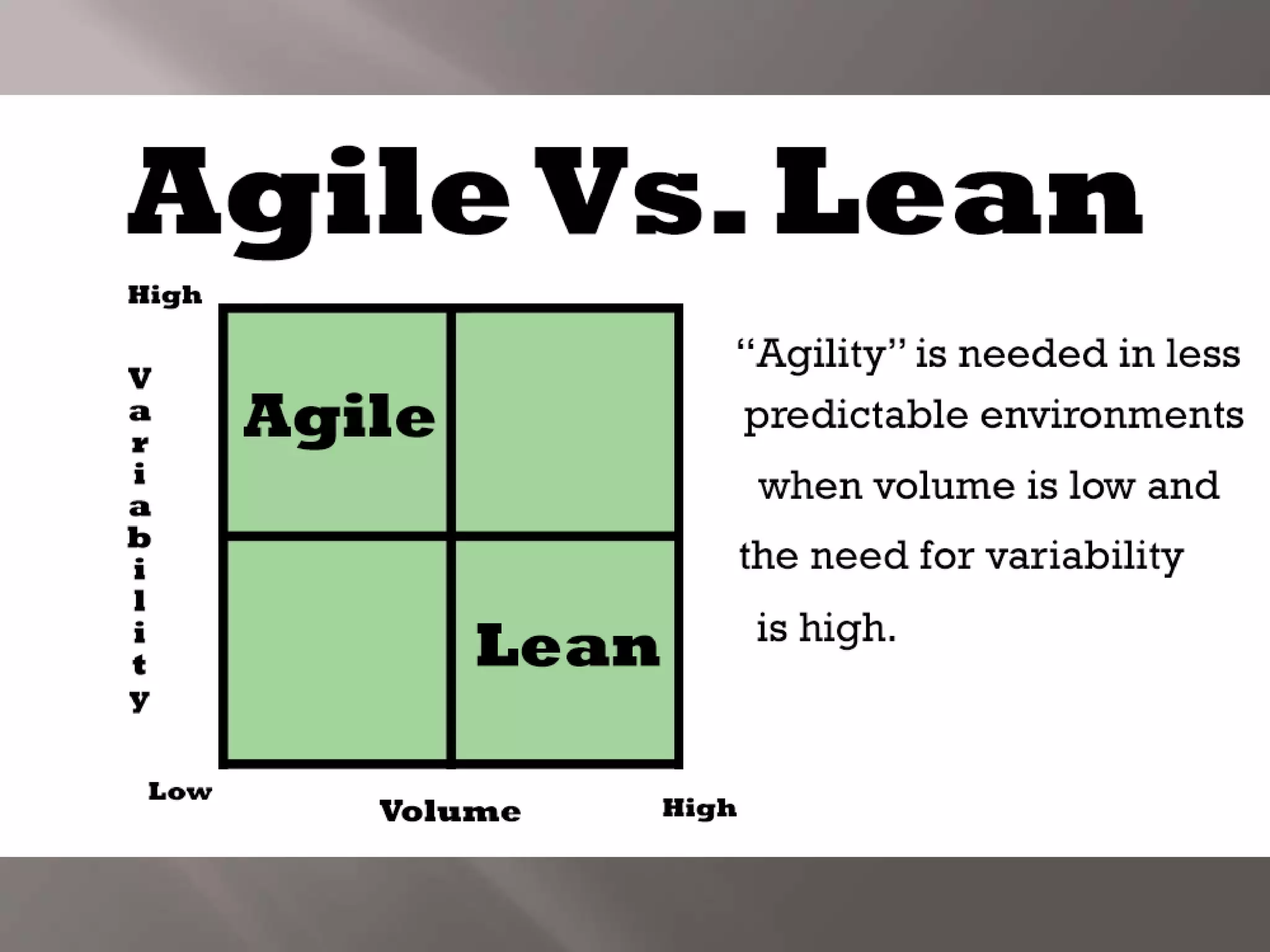
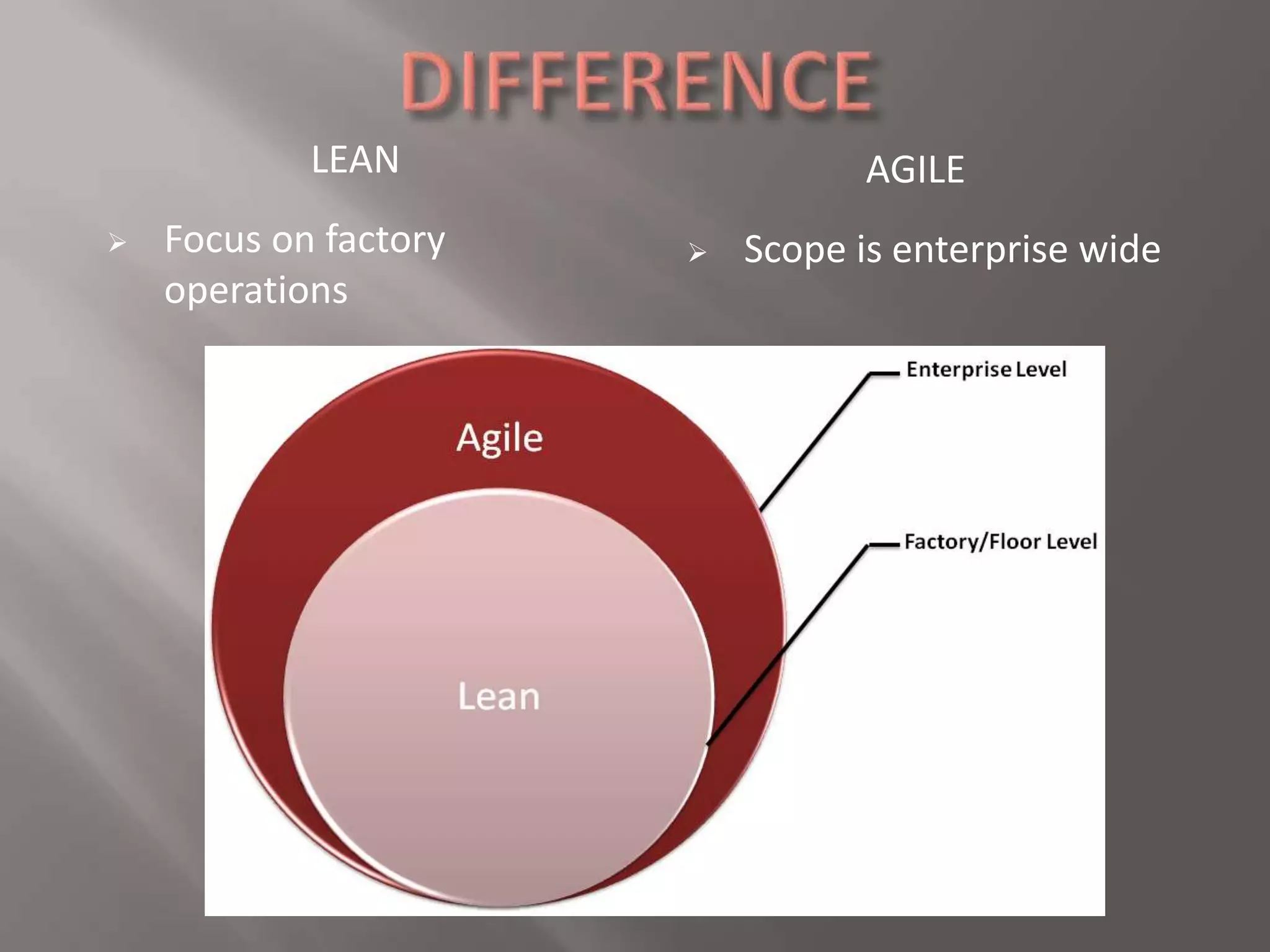
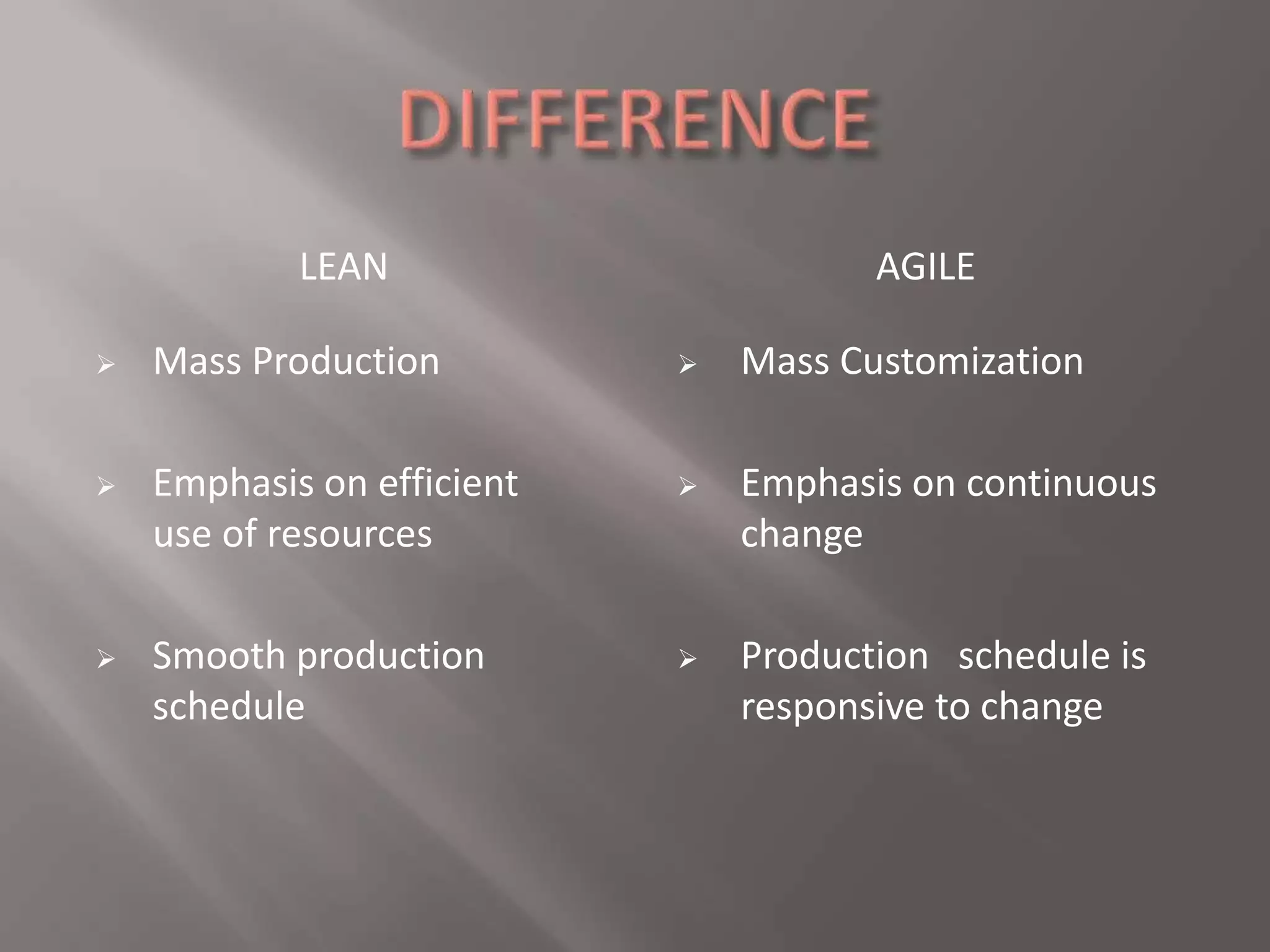
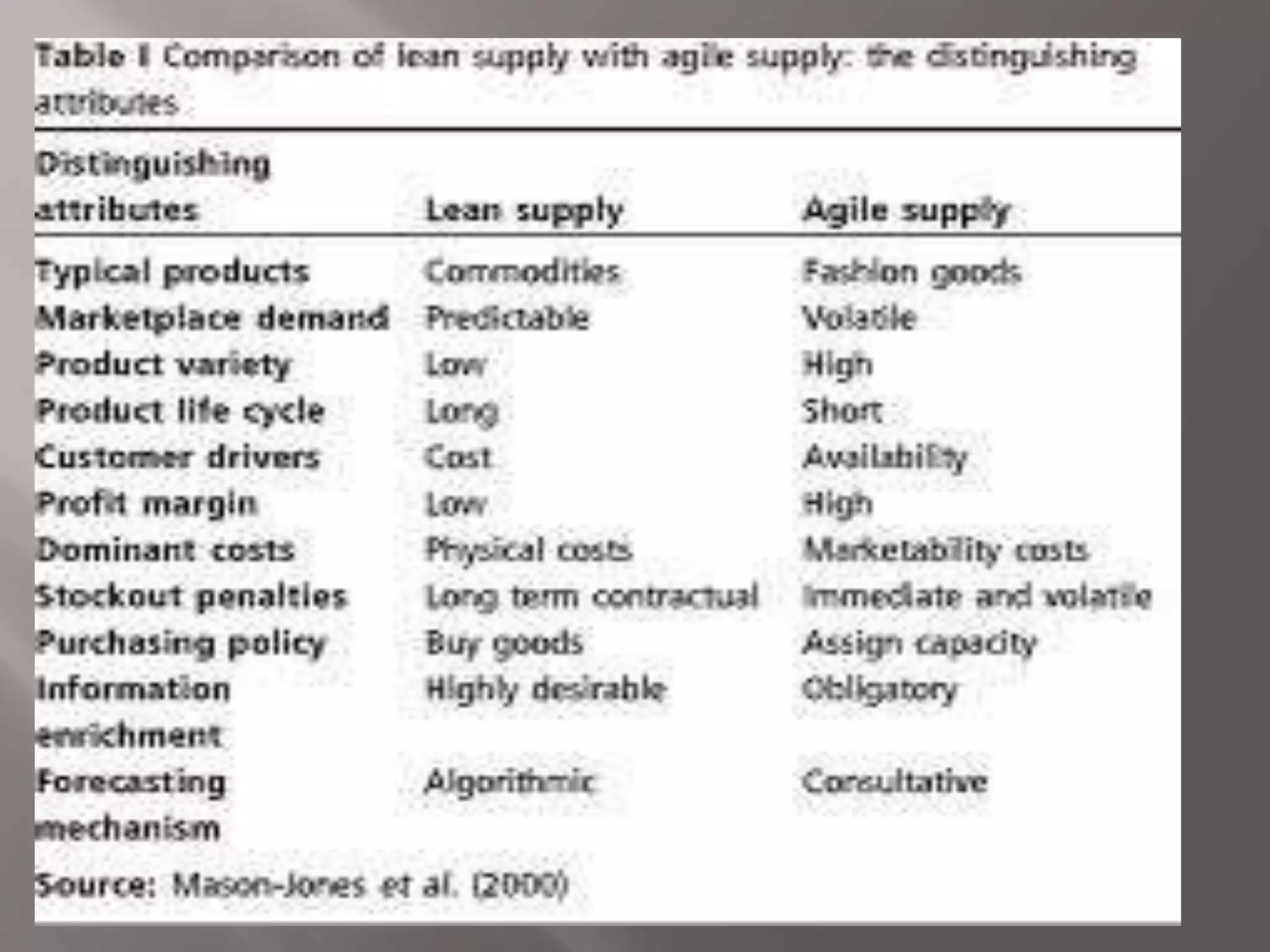
Lean manufacturing aims to eliminate waste by focusing on adding value for the customer. It considers any expenditure that does not directly create customer value to be wasteful. Agile manufacturing allows organizations to quickly respond to customer needs and market changes while controlling costs and quality. It is seen as the next step after lean manufacturing in evolving production methods. Both lean and agile manufacturing ultimately aim to increase business sustainability in manufacturing through efficient use of resources and responsiveness to customers.