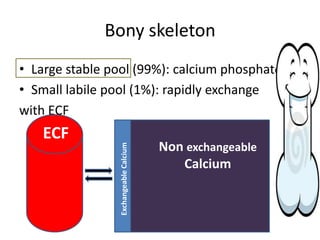
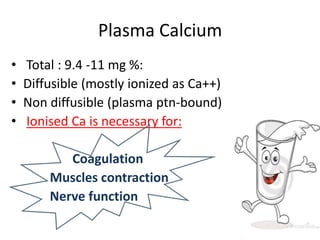
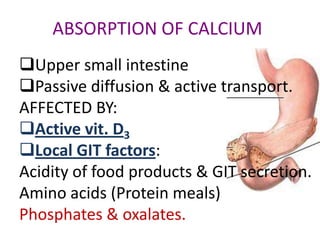
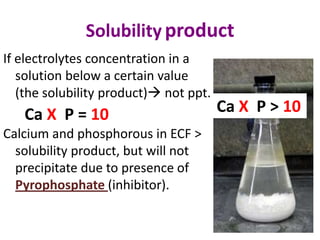
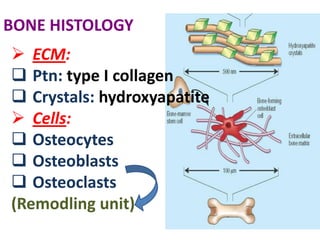
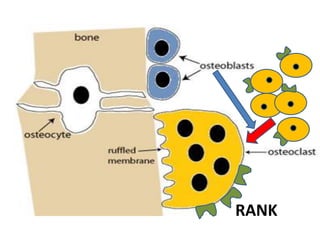
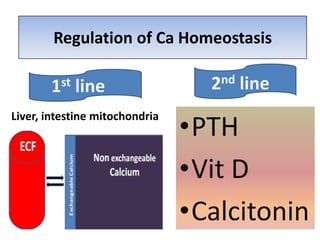
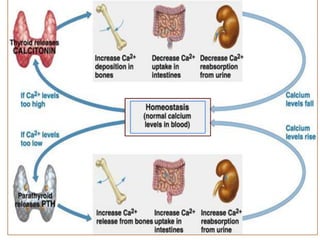
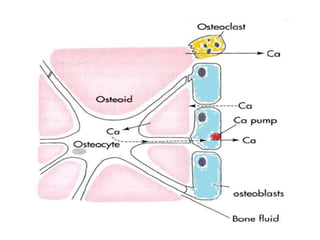
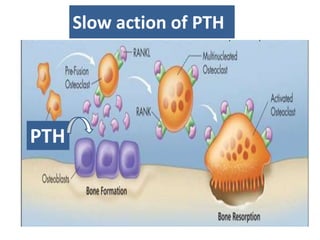
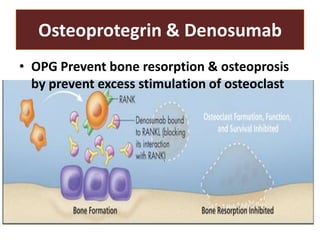
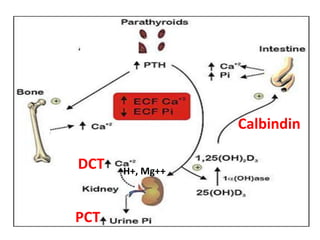
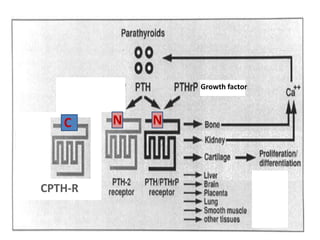
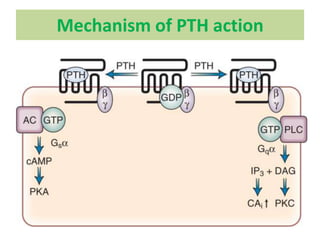
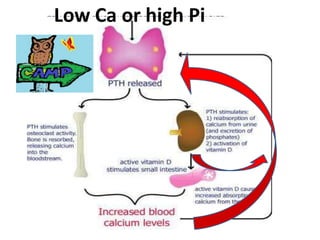
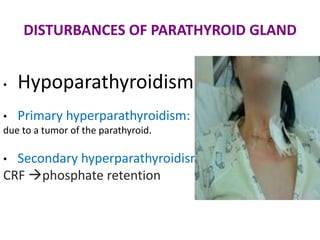
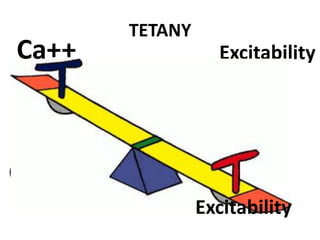
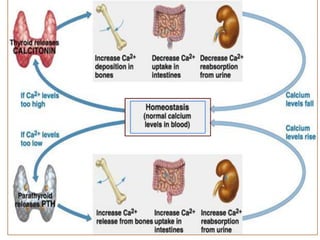
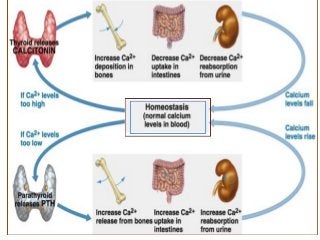
This document discusses calcium homeostasis and the roles of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and vitamin D3. It covers calcium distribution in the body, absorption in the small intestine, and regulation of calcium levels. PTH acts on bone to increase calcium levels by promoting bone resorption. Vitamin D3 aids in calcium absorption from the gut. Disturbances in PTH can cause hyperparathyroidism or hypoparathyroidism and the resulting condition of tetany.