1. Prolonged immobility can lead to serious physical and psychological complications for older adults due to deconditioning and loss of mobility.
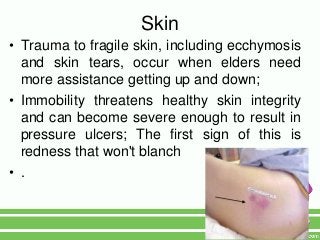
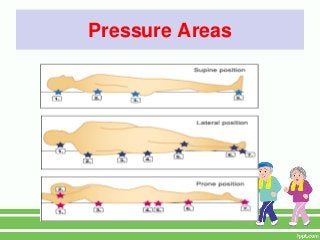
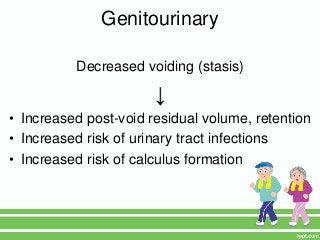
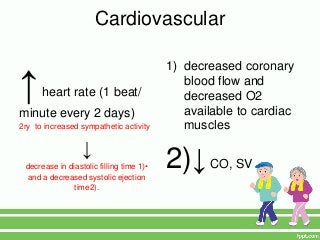
2. Key physical risks include muscle atrophy, bone loss, skin breakdown, cardiovascular deconditioning, pulmonary issues, and functional decline.
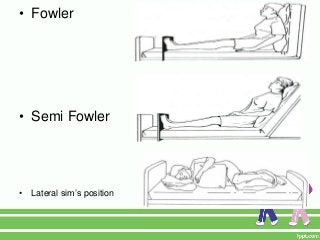
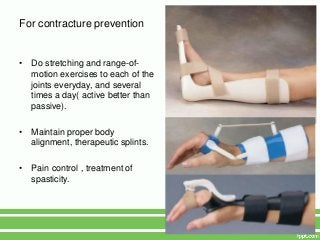
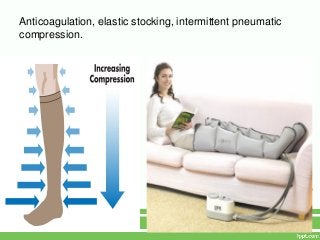
3. Interventions like range of motion exercises, proper positioning, ambulation assistance, and pain management can help mitigate risks while immobilization is necessary. Regular mobility is important for overall health in older adults.