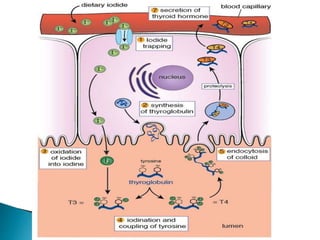
Ms. Anu Sebastian is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Pharmacology at Nirmala College of Pharmacy in Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, Kerala. The document outlines the 8 key steps in the synthesis of thyroid hormones: 1) Iodide trapping, 2) Thyroglobulin synthesis, 3) Iodide oxidation, 4) Iodination of tyrosine, 5) Coupling of monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine, 6) Pinocytosis and digestion of colloid droplets, 7) Secretion of thyroid hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine into blood circulation, and 8) Transport of hormones via thyroxine binding proteins in the