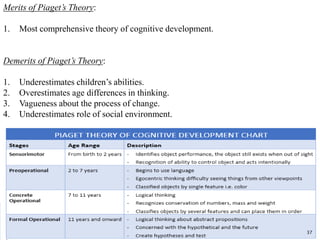
The document outlines key psychodynamic theories relevant to child psychology, including Freud's psychoanalytical theory, Erikson's psychosocial model, and Piaget's cognitive theory. It discusses the stages of development as defined by these theorists, highlighting the influence of these stages on behavior and psychological development. Additionally, it critiques the theories for their limitations while recognizing their contributions to understanding child development.