The document provides an overview of child psychology and its relevance to dentistry. It discusses several theories of child development, including Freud's psychosexual stages of development, Erikson's psychosocial stages, and Piaget's cognitive development stages. According to these theories, a child's psychological development progresses through distinct phases, and their experiences at each phase shape their behaviors and personality. Understanding child psychology is important for dental clinicians to effectively communicate with children, gain their confidence, and create a comfortable environment during treatments. The document also covers definitions, factors influencing child behavior, and behavioral management strategies.






![THEORIES OF CHILD PSYCHOLOGY
A] Psychodynamic theories
1.Psychosexual/Psychoanalytic theory
Sigmund Freud (1905)
2.Cognitive theory
Jean Piaget (1952)
3.Psychosocial theory
V - Erik Erickson (1963)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-7-2048.jpg)
![B] Theories of learning and behavior development
1. Classical conditioning - Pavlov (1927)
2. Operant conditioning - Skinner (1938)
3. Hierarchy of needs - Maslow (1954)
4. Social learning theory - Bandura (1963)
C] Margaret Mahler's theory of development (1933)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-8-2048.jpg)


![a] Topographic model
• There are 3 levels of consciousness:
• Conscious - a part of personality which is aware of thoughts
and feelings for basic activities
• Preconscious - a part of personality of which the individual is
not aware of at the moment however able to recollect into
awareness without great difficulty.
• Subconscious/unconscious - part of personality of which .
individual is unaware, which generally cannot bring into
awareness without help of assistant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-11-2048.jpg)


































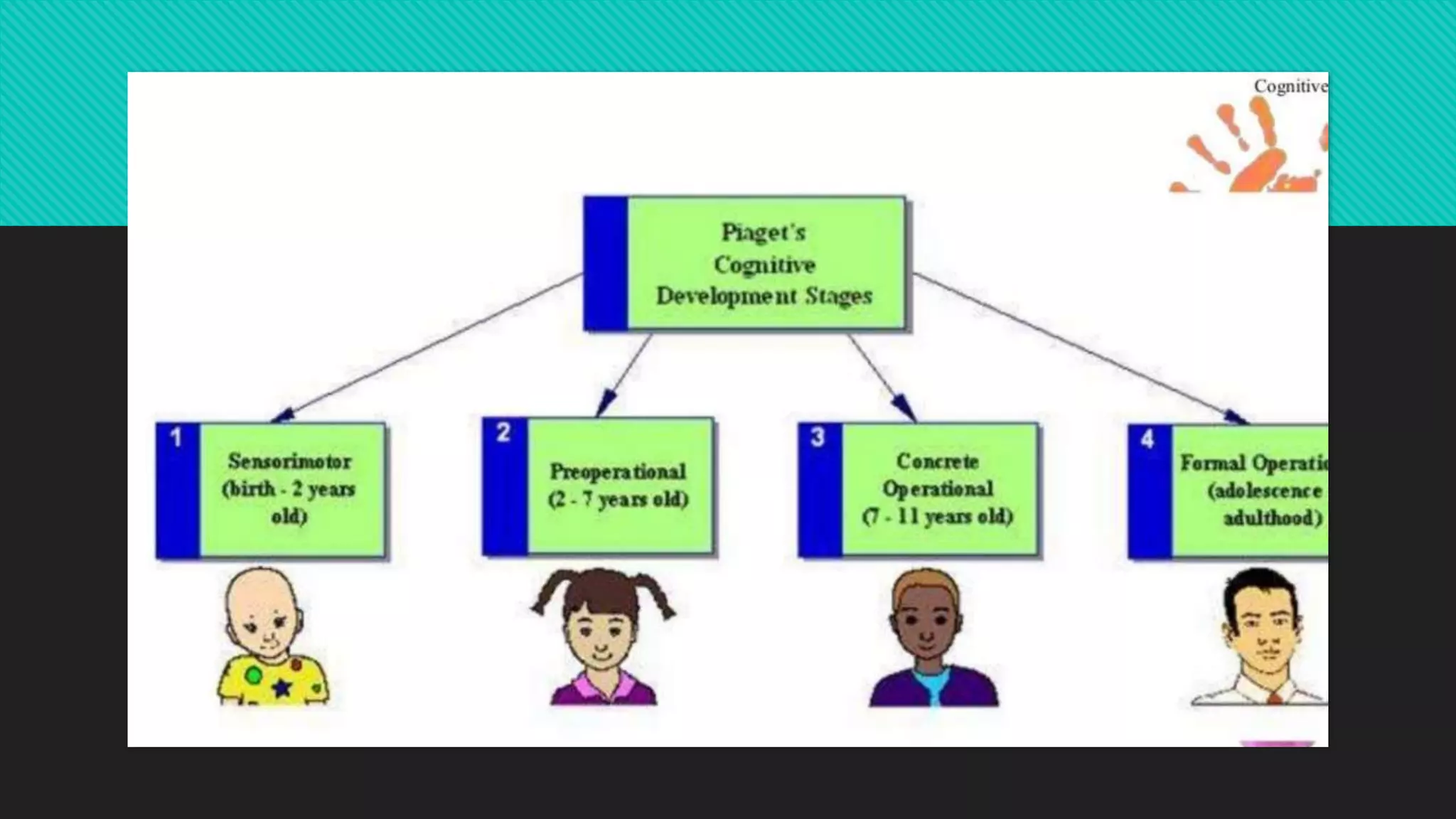



![B] Preoperational stage (2 to 6yrs)
• Primitive strategies changes as the child assimilates new experiences
and accommodates original strategies.
• The child uses symbols in language with play.
• Learns to classify things.
• Solves problems as a result of intuitive thinking but / cannot explain
why
• Concept of egocentrism
• Unaware of others perspective](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-50-2048.jpg)
































![Behavior shaping
1] Desensitization
• Joseph Wolpe (1975)
• It is accompanied by teaching the child a competing
response such as relaxing and then introducing a
threatening stimuli](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-83-2048.jpg)

![2] Modeling
• Bandura in 1969
• Social learning principle
• Modelling can be done by
• Live models - siblings, parents of child etc.,
• Filmed models
• Posters
• Audio - visual aids.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-85-2048.jpg)
![3] Contingency management
• Method of modifying the behavior by presentation or withdrawal of
reinforcers
• A +ve reinforcers: Henry W Fields in 1984. In this the contingent
presentation increases the frequency of behavior.
• B -ve rein forcers: Stokes and Kennedy in 1980. In this, the contingent
withdrawal increases the frequency of behavior this is generally a
termination of an aversive stimulus. E.g. withdrawal of the mother.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chilpsychologypk-210215184437/75/Child-psychology-child-behavioural-management-86-2048.jpg)



