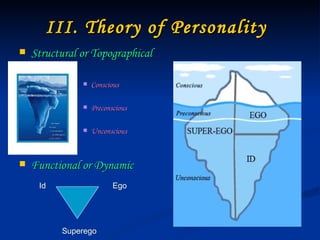
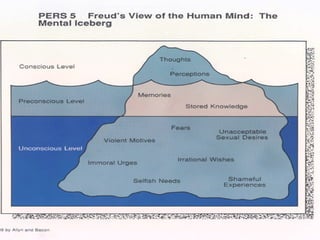
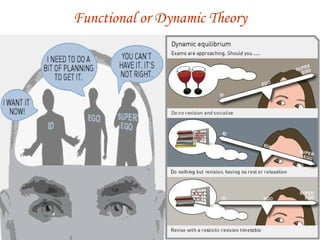
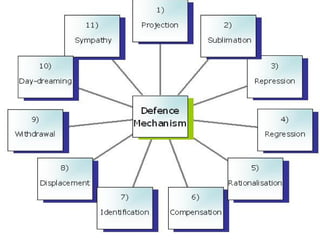
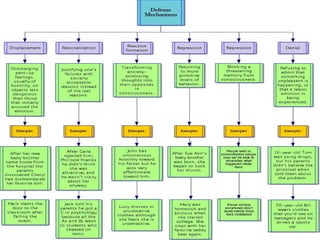
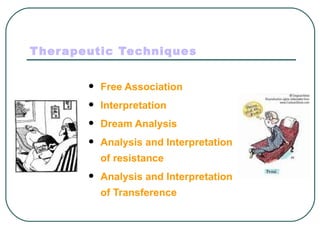
Sigmund Freud developed psychoanalysis and its fundamental assumptions include that unconscious factors motivate behavior, early childhood experiences shape personality, and unconscious motives and conflicts are central. His basic concepts include human nature being determined by unconscious drives, instincts being life instincts and death instincts, and the structural theory of personality comprising the conscious, preconscious, and unconscious. Defense mechanisms like repression are employed by the ego to reduce anxiety from unconscious conflicts. Psychoanalysis aims to make the unconscious conscious through techniques like free association, dream analysis, and interpretation of transference.